Page 247 - Boiler plant and distribution system optimization manual
P. 247
232 Boiler Plant and Distribution System Optimization Manual
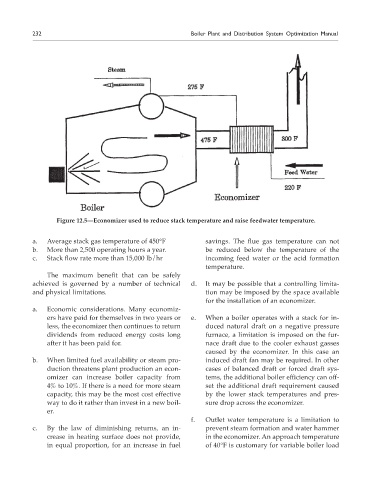
Figure 12.5—Economizer used to reduce stack temperature and raise feedwater temperature.
a. Average stack gas temperature of 450°F savings. The flue gas temperature can not
b. More than 2,500 operating hours a year. be reduced below the temperature of the
c. Stack flow rate more than 15,000 lb/hr incoming feed water or the acid formation
temperature.
The maximum benefit that can be safely
achieved is governed by a number of technical d. It may be possible that a controlling limita-
and physical limitations. tion may be imposed by the space available
for the installation of an economizer.
a. Economic considerations. Many economiz-
ers have paid for themselves in two years or e. When a boiler operates with a stack for in-
less, the economizer then continues to return duced natural draft on a negative pressure
dividends from reduced energy costs long furnace, a limitation is imposed on the fur-
after it has been paid for. nace draft due to the cooler exhaust gasses
caused by the economizer. In this case an
b. When limited fuel availability or steam pro- induced draft fan may be required. In other
duction threatens plant production an econ- cases of balanced draft or forced draft sys-
omizer can increase boiler capacity from tems, the additional boiler efficiency can off-
4% to 10%. If there is a need for more steam set the additional draft requirement caused
capacity, this may be the most cost effective by the lower stack temperatures and pres-
way to do it rather than invest in a new boil- sure drop across the economizer.
er.
f. Outlet water temperature is a limitation to
c. By the law of diminishing returns, an in- prevent steam formation and water hammer
crease in heating surface does not provide, in the economizer. An approach temperature
in equal proportion, for an increase in fuel of 40°F is customary for variable boiler load