Page 301 - Boiler plant and distribution system optimization manual
P. 301
286 Boiler Plant and Distribution System Optimization Manual
the boiler water. The metal tubes in the boiler are water. These solids are not evaporated with the
kept cool by the boiler water. When scale forms, it steam; as a result the TDS becomes more concen-
acts like an insulation material between the water trated as more steam is generated.
and the metal. This results in tubes operating at The level to which the TDS will concentrate
higher temperatures. The greater the thickness of is determined by the amount of these salts re-
the scale, the greater the insulating effect, and the moved in the blowdown. Control of TDS level is
higher the temperature of the tubes. At sufficient- critical in boiler operation. The higher TDS levels
ly high temperatures, the tube can lose tensile result in higher boiler efficiencies, but TDS levels
strength and rupture. that are too high will interfere with boiler opera-
tion.
Sludges
Sludges are precipitated directly in the main The Consequences of Too Little Blowdown
body of the boiler water when their solubilities TDS Too High
are exceeded. Sludge deposition usually occurs • Corrosive to boiler metal
when binders are present or when water circula- • Causes foaming and carryover
tion is such that it allows sludge settling on hot • Alters boiling patterns in tubes leading
spots allowing it to “bake” on to hot surfaces. to deposits.
TDS in a Boiler Suspended Solids and
TDS in a boiler is one of the parameters used Sludge too High
to control the water treatment program. Dissolved • Bakes onto heat transfer surfaces causing
solids are continually added to the boiler makeup lost efficiency.
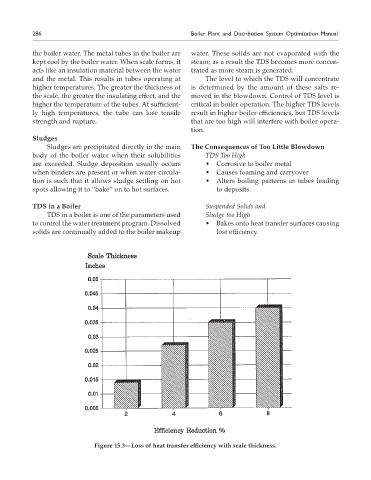
Figure 15.3—Loss of heat transfer efficiency with scale thickness.