Page 169 - Building Big Data Applications
P. 169
168 Building Big Data Applications
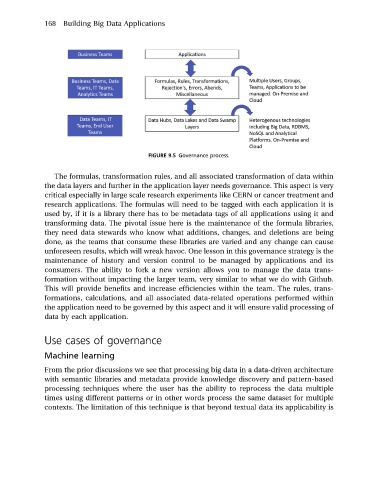
FIGURE 9.5 Governance process.
The formulas, transformation rules, and all associated transformation of data within
the data layers and further in the application layer needs governance. This aspect is very
critical especially in large scale research experiments like CERN or cancer treatment and
research applications. The formulas will need to be tagged with each application it is
used by, if it is a library there has to be metadata tags of all applications using it and
transforming data. The pivotal issue here is the maintenance of the formula libraries,
they need data stewards who know what additions, changes, and deletions are being
done, as the teams that consume these libraries are varied and any change can cause
unforeseen results, which will wreak havoc. One lesson in this governance strategy is the
maintenance of history and version control to be managed by applications and its
consumers. The ability to fork a new version allows you to manage the data trans-
formation without impacting the larger team, very similar to what we do with Github.
This will provide benefits and increase efficiencies within the team. The rules, trans-
formations, calculations, and all associated data-related operations performed within
the application need to be governed by this aspect and it will ensure valid processing of
data by each application.
Use cases of governance
Machine learning
From the prior discussions we see that processing big data in a data-driven architecture
with semantic libraries and metadata provide knowledge discovery and pattern-based
processing techniques where the user has the ability to reprocess the data multiple
times using different patterns or in other words process the same dataset for multiple
contexts. The limitation of this technique is that beyond textual data its applicability is