Page 123 -
P. 123
122 Part II • Descriptive Analytics
Web pages
Application
server
Client Web
(Web browser) Internet/ server
Intranet/
Extranet
Data
warehouse
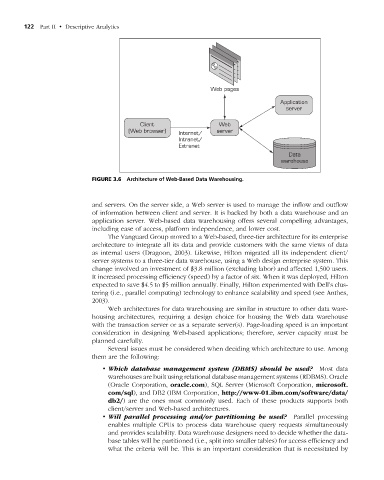
figure 3.6 Architecture of Web-Based Data Warehousing.
and servers. On the server side, a Web server is used to manage the inflow and outflow
of information between client and server. It is backed by both a data warehouse and an
application server. Web-based data warehousing offers several compelling advantages,
including ease of access, platform independence, and lower cost.
The Vanguard Group moved to a Web-based, three-tier architecture for its enterprise
architecture to integrate all its data and provide customers with the same views of data
as internal users (Dragoon, 2003). Likewise, Hilton migrated all its independent client/
server systems to a three-tier data warehouse, using a Web design enterprise system. This
change involved an investment of $3.8 million (excluding labor) and affected 1,500 users.
It increased processing efficiency (speed) by a factor of six. When it was deployed, Hilton
expected to save $4.5 to $5 million annually. Finally, Hilton experimented with Dell’s clus-
tering (i.e., parallel computing) technology to enhance scalability and speed (see Anthes,
2003).
Web architectures for data warehousing are similar in structure to other data ware-
housing architectures, requiring a design choice for housing the Web data warehouse
with the transaction server or as a separate server(s). Page-loading speed is an important
consideration in designing Web-based applications; therefore, server capacity must be
planned carefully.
Several issues must be considered when deciding which architecture to use. Among
them are the following:
• Which database management system (DBMS) should be used? Most data
warehouses are built using relational database management systems (RDBMS). Oracle
(Oracle Corporation, oracle.com), SQL Server (Microsoft Corporation, microsoft.
com/sql), and DB2 (IBM Corporation, http://www-01.ibm.com/software/data/
db2/) are the ones most commonly used. Each of these products supports both
client/server and Web-based architectures.
• Will parallel processing and/or partitioning be used? Parallel processing
enables multiple CPUs to process data warehouse query requests simultaneously
and provides scalability. Data warehouse designers need to decide whether the data-
base tables will be partitioned (i.e., split into smaller tables) for access efficiency and
what the criteria will be. This is an important consideration that is necessitated by
M03_SHAR9209_10_PIE_C03.indd 122 1/25/14 7:35 AM