Page 198 -
P. 198
Chapter 4 • Business Reporting, Visual Analytics, and Business Performance Management 197
Strategy
1. Strategize 2. Plan
Mission, values, goals, Budgets, plans, forecasts,
objectives, incentives,
strategy maps
targets
models, initiatives,
Integrated
Data and
Metrics
Performance dashboards,
reports, analytical tools
Interpret,
3. Monitor/Analyze
collaborate, assess,
decide, act, adjust, track
4. Act/Adjust
Execution
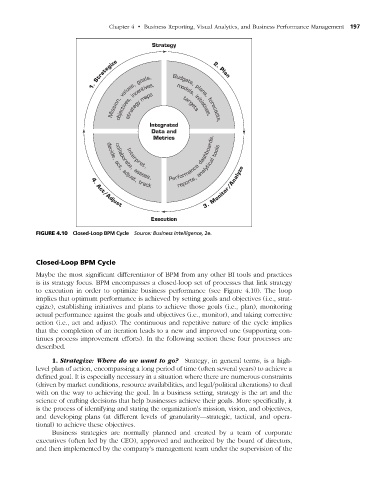
figuRe 4.10 Closed-Loop BPM Cycle Source: Business Intelligence, 2e.
Closed-loop BpM Cycle
Maybe the most significant differentiator of BPM from any other BI tools and practices
is its strategy focus. BPM encompasses a closed-loop set of processes that link strategy
to execution in order to optimize business performance (see Figure 4.10). The loop
implies that optimum performance is achieved by setting goals and objectives (i.e., strat-
egize), establishing initiatives and plans to achieve those goals (i.e., plan), monitoring
actual performance against the goals and objectives (i.e., monitor), and taking corrective
action (i.e., act and adjust). The continuous and repetitive nature of the cycle implies
that the completion of an iteration leads to a new and improved one (supporting con-
tinues process improvement efforts). In the following section these four processes are
described.
1. Strategize: Where do we want to go? Strategy, in general terms, is a high-
level plan of action, encompassing a long period of time (often several years) to achieve a
defined goal. It is especially necessary in a situation where there are numerous constraints
(driven by market conditions, resource availabilities, and legal/political alterations) to deal
with on the way to achieving the goal. In a business setting, strategy is the art and the
science of crafting decisions that help businesses achieve their goals. More specifically, it
is the process of identifying and stating the organization’s mission, vision, and objectives,
and developing plans (at different levels of granularity—strategic, tactical, and opera-
tional) to achieve these objectives.
Business strategies are normally planned and created by a team of corporate
executives (often led by the CEO), approved and authorized by the board of directors,
and then implemented by the company’s management team under the supervision of the
M04_SHAR9209_10_PIE_C04.indd 197 1/25/14 7:34 AM