Page 46 -
P. 46
Chapter 1 • An Overview of Business Intelligence, Analytics, and Decision Support 45
Querying and ETL
reporting
Metadata Data warehouse
DSS
EIS/ESS
Data marts Spreadsheets
Financial (MS Excel)
reporting
OLAP
Digital cockpits
and dashboards Business
intelligence
Scorecards and
dashboards
Workflow
Alerts and
notifications
Data & text
mining Predictive Broadcasting
analytics tools Portals
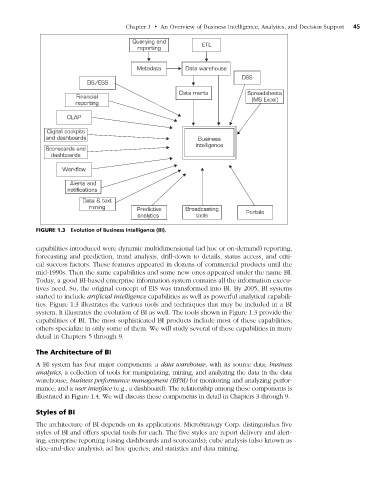
Figure 1.3 Evolution of Business Intelligence (BI).
capabilities introduced were dynamic multidimensional (ad hoc or on-demand) reporting,
forecasting and prediction, trend analysis, drill-down to details, status access, and criti-
cal success factors. These features appeared in dozens of commercial products until the
mid-1990s. Then the same capabilities and some new ones appeared under the name BI.
Today, a good BI-based enterprise information system contains all the information execu-
tives need. So, the original concept of EIS was transformed into BI. By 2005, BI systems
started to include artificial intelligence capabilities as well as powerful analytical capabili-
ties. Figure 1.3 illustrates the various tools and techniques that may be included in a BI
system. It illustrates the evolution of BI as well. The tools shown in Figure 1.3 provide the
capabilities of BI. The most sophisticated BI products include most of these capabilities;
others specialize in only some of them. We will study several of these capabilities in more
detail in Chapters 5 through 9.
the architecture of Bi
A BI system has four major components: a data warehouse, with its source data; business
analytics, a collection of tools for manipulating, mining, and analyzing the data in the data
warehouse; business performance management (BPM) for monitoring and analyzing perfor-
mance; and a user interface (e.g., a dashboard). The relationship among these components is
illustrated in Figure 1.4. We will discuss these components in detail in Chapters 3 through 9.
styles of Bi
The architecture of BI depends on its applications. MicroStrategy Corp. distinguishes five
styles of BI and offers special tools for each. The five styles are report delivery and alert-
ing; enterprise reporting (using dashboards and scorecards); cube analysis (also known as
slice-and-dice analysis); ad hoc queries; and statistics and data mining.
M01_SHAR9209_10_PIE_C01.indd 45 1/25/14 7:46 AM