Page 47 -
P. 47
46 Part I • Decision Making and Analytics: An Overview
Data Warehouse Business Analytics Performance and
Environment Environment Strategy
Data
Sources Technical staff Business users
Build the data warehouse Access Managers/executives
Data
Organizing warehouse Manipulation, results BPM strategies
Summarizing
Standardizing
User interface
Future component: Browser
intelligent systems Portal
Dashboard
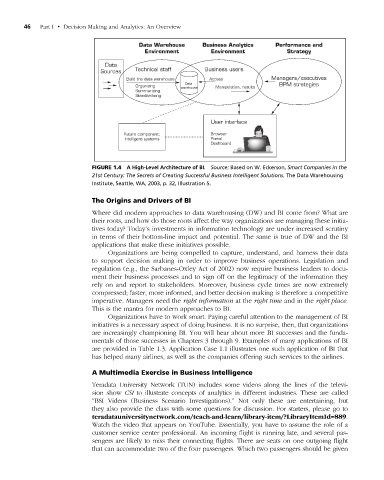
Figure 1.4 A High-Level Architecture of BI. Source: Based on W. eckerson, Smart Companies in the
21st Century: The Secrets of Creating Successful Business Intelligent Solutions. the Data Warehousing
Institute, Seattle, Wa, 2003, p. 32, Illustration 5.
the origins and drivers of Bi
Where did modern approaches to data warehousing (DW) and BI come from? What are
their roots, and how do those roots affect the way organizations are managing these initia-
tives today? Today’s investments in information technology are under increased scrutiny
in terms of their bottom-line impact and potential. The same is true of DW and the BI
applications that make these initiatives possible.
Organizations are being compelled to capture, understand, and harness their data
to support decision making in order to improve business operations. Legislation and
regulation (e.g., the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002) now require business leaders to docu-
ment their business processes and to sign off on the legitimacy of the information they
rely on and report to stakeholders. Moreover, business cycle times are now extremely
compressed; faster, more informed, and better decision making is therefore a competitive
imperative. Managers need the right information at the right time and in the right place.
This is the mantra for modern approaches to BI.
Organizations have to work smart. Paying careful attention to the management of BI
initiatives is a necessary aspect of doing business. It is no surprise, then, that organizations
are increasingly championing BI. You will hear about more BI successes and the funda-
mentals of those successes in Chapters 3 through 9. Examples of many applications of BI
are provided in Table 1.3. Application Case 1.1 illustrates one such application of BI that
has helped many airlines, as well as the companies offering such services to the airlines.
a multimedia exercise in Business intelligence
Teradata University Network (TUN) includes some videos along the lines of the televi-
sion show CSI to illustrate concepts of analytics in different industries. These are called
“BSI Videos (Business Scenario Investigations).” Not only these are entertaining, but
they also provide the class with some questions for discussion. For starters, please go to
teradatauniversitynetwork.com/teach-and-learn/library-item/?Libraryitemid=889.
Watch the video that appears on YouTube. Essentially, you have to assume the role of a
customer service center professional. An incoming flight is running late, and several pas-
sengers are likely to miss their connecting flights. There are seats on one outgoing flight
that can accommodate two of the four passengers. Which two passengers should be given
M01_SHAR9209_10_PIE_C01.indd 46 1/25/14 7:46 AM