Page 91 -
P. 91
90 Part I • Decision Making and Analytics: An Overview
14 1
Stand-alone, Semistructured 2
integration, and or unstructured Support
Web-based problems managers at
13 all levels
Data access 3
Support
individuals
12 and groups
Modeling 4
and analysis
Interdependent
or sequential
11 Decision Support decisions
Ease of Systems (DSS)
development 5
by end users Support
intelligence
10 design, choice, and
implementation
Humans control 6
the process
Support variety
of decision
9 processes and styles
Effectiveness 8 7
and efficiency
Interactive, Adaptable
ease of use and flexible
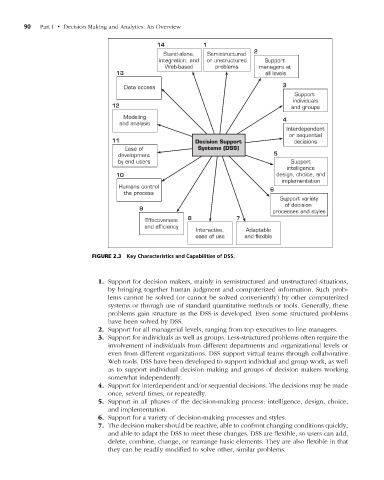
figure 2.3 Key Characteristics and Capabilities of DSS.
1. Support for decision makers, mainly in semistructured and unstructured situations,
by bringing together human judgment and computerized information. Such prob-
lems cannot be solved (or cannot be solved conveniently) by other computerized
systems or through use of standard quantitative methods or tools. Generally, these
problems gain structure as the DSS is developed. Even some structured problems
have been solved by DSS.
2. Support for all managerial levels, ranging from top executives to line managers.
3. Support for individuals as well as groups. Less-structured problems often require the
involvement of individuals from different departments and organizational levels or
even from different organizations. DSS support virtual teams through collaborative
Web tools. DSS have been developed to support individual and group work, as well
as to support individual decision making and groups of decision makers working
somewhat independently.
4. Support for interdependent and/or sequential decisions. The decisions may be made
once, several times, or repeatedly.
5. Support in all phases of the decision-making process: intelligence, design, choice,
and implementation.
6. Support for a variety of decision-making processes and styles.
7. The decision maker should be reactive, able to confront changing conditions quickly,
and able to adapt the DSS to meet these changes. DSS are flexible, so users can add,
delete, combine, change, or rearrange basic elements. They are also flexible in that
they can be readily modified to solve other, similar problems.
M02_SHAR9209_10_PIE_C02.indd 90 1/25/14 7:45 AM