Page 254 - Calculus Workbook For Dummies
P. 254
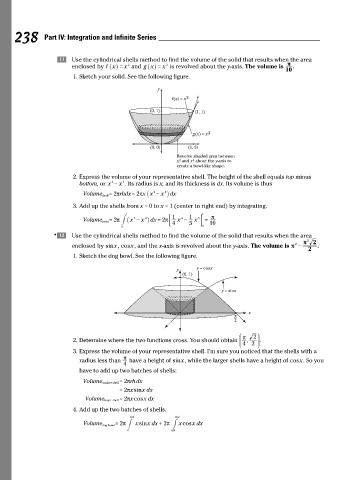
238 Part IV: Integration and Infinite Series
k Use the cylindrical shells method to find the volume of the solid that results when the area
3
2
enclosed by f x = x and g x = x is revolved about the y-axis. The volume is π .
^ h
^ h
10
1. Sketch your solid. See the following figure.
y
f(x) = x 2
(0, 1) (1, 1)
g(x) = x 3
(0, 0) (1, 0)
Revolve shaded area between
x 2 and x 3 about the y-axis to
create a bowl-like shape.
2. Express the volume of your representative shell. The height of the shell equals top minus
2
3
bottom, or x - x . Its radius is x, and its thickness is dx. Its volume is thus
3
x x -
=
Volume shell = 2 π rhdx 2 π _ 2 x i dx
3. Add up the shells from x = 0 to x = 1 (center to right end) by integrating.
1 1 π
π
4
3
4
5
Volume bowl = 2 π # _ x - x i dx 2 ; 1 x - 1 x E =
=
4 5 10
0 0
*l Use the cylindrical shells method to find the volume of the solid that results when the area
2 2
π
2
enclosed by sinx, cosx, and the x-axis is revolved about the y-axis. The volume is π - .
2
1. Sketch the dog bowl. See the following figure.
y y = cosx
(0, 1)
y = sinx
x
π
2
J N
2
2. Determine where the two functions cross. You should obtain K K π , 2 O O .
L 4 P
3. Express the volume of your representative shell. I’m sure you noticed that the shells with a
π
radius less than have a height of sinx, while the larger shells have a height of cosx. So you
4
have to add up two batches of shells:
Volume smaller shell= 2 π rhdx
= 2 π x sinx dx
er shell= 2 π x cosx dx
Volume argl
4. Add up the two batches of shells.
/ π 4 / π 2
Volume dog bowl = 2 π # x sinx dx + 2 π x # cosx dx
0 / π 4