Page 195 - Cam Design Handbook
P. 195
THB7 8/15/03 1:58 PM Page 183
GEOMETRY OF PLANAR CAM PROFILES 183
¢
P (q)
O 2 P (q)
¢¢
2
P (q)
2
P 2
P (q)
1
¢
P (q)
1
¢¢
P (q) P 1
1
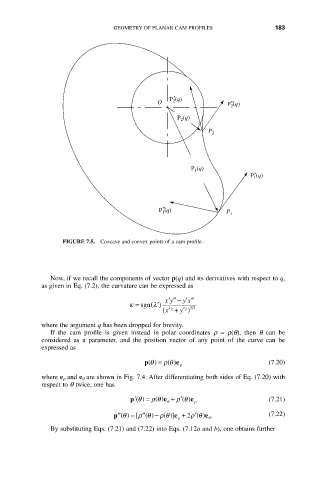
FIGURE 7.5. Concave and convex points of a cam profile.
Now, if we recall the components of vector p(q) and its derivatives with respect to q,
as given in Eq. (7.2), the curvature can be expressed as
¢¢¢ - ¢¢¢
xy yx
k = sgn ()
l¢
2
y
2
(x ¢ + ¢ ) 32
where the argument q has been dropped for brevity.
If the cam profile is given instead in polar coordinates r = r(q), then q can be
considered as a parameter, and the position vector of any point of the curve can be
expressed as
p q () = () e r (7.20)
r q
where e r and e q are shown in Fig. 7.4. After differentiating both sides of Eq. (7.20) with
respect to q twice, one has
p ¢() = ()eq r q q + ¢()e r (7.21)
r
q
¢¢() = [r
p q ¢¢() - ()]eq r q r + r ¢()eq q . (7.22)
2
By substituting Eqs. (7.21) and (7.22) into Eqs. (7.12a and b), one obtains further