Page 42 - Cam Design Handbook
P. 42
THB2 8/15/03 12:48 PM Page 30
30 CAM DESIGN HANDBOOK
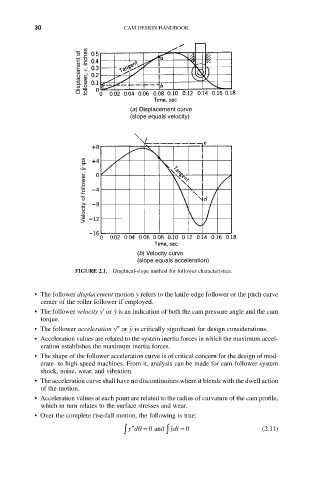
Displacement of follower, y, inches
(a) Displacement curve
(slope equals velocity)
Velocity of follower, y ips
(b) Velocity curve
(slope equals acceleration)
FIGURE 2.1. Graphical-slope method for follower characteristics.
• The follower displacement motion y refers to the knife-edge follower or the pitch curve
center of the roller follower if employed.
˙ y
• The follower velocity y¢ or is an indication of both the cam pressure angle and the cam
torque.
˙˙ y
• The follower acceleration y≤ or is critically significant for design considerations.
• Acceleration values are related to the system inertia forces in which the maximum accel-
eration establishes the maximum inertia forces.
• The shape of the follower acceleration curve is of critical concern for the design of mod-
erate- to high-speed machines. From it, analysis can be made for cam-follower system
shock, noise, wear, and vibration.
• The acceleration curve shall have no discontinuities where it blends with the dwell action
of the motion.
• Acceleration values at each point are related to the radius of curvature of the cam profile,
which in turn relates to the surface stresses and wear.
• Over the complete rise-fall motion, the following is true:
Ú
Ú ¢¢ ydq = 0 and ˙˙ = 0 (2.11)
ydt