Page 96 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 96
88 Carbon Nanotube Fibers and Yarns
90 50
T300 T300
IM7 IM7
GT PAN GT PAN
GT PAN/CNT(0.42%) 40 GT PAN/CNT(0.42%)
GT PAN/CNT(0.5%)
Electrical conductivity (kS/m) 70 Thermal conductivity (W/m-k) 30
GT PAN/CNT(0.5%)
GT PAN/CNT(1.0%)
GT PAN/CNT(1.0%)
80
20
60
50 10
280 290 300 310 320 330 340 350 280 290 300 310 320 330 340 350
(A) Temperature (K) (B) Temperature (K)
Carbon fiber diameter (µm)
1 10
8
Carbonized PAN
7 Carbonized PAN/CNT (99/1)
6
Tensile strength (GPa) 5 4 3
2
1
0
0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000
(C) Cross-sectional area (µm )
2
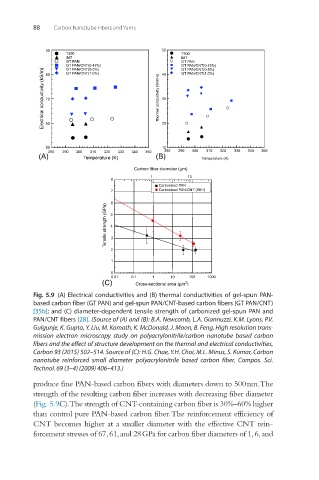
Fig. 5.9 (A) Electrical conductivities and (B) thermal conductivities of gel-spun PAN-
based carbon fiber (GT PAN) and gel-spun PAN/CNT-based carbon fibers (GT PAN/CNT)
[35b]; and (C) diameter-dependent tensile strength of carbonized gel-spun PAN and
PAN/CNT fibers [28]. (Source of (A) and (B): B.A. Newcomb, L.A. Giannuzzi, K.M. Lyons, P.V.
Gulgunje, K. Gupta, Y. Liu, M. Kamath, K. McDonald, J. Moon, B. Feng, High resolution trans-
mission electron microscopy study on polyacrylonitrile/carbon nanotube based carbon
fibers and the effect of structure development on the thermal and electrical conductivities,
Carbon 93 (2015) 502–514. Source of (C): H.G. Chae, Y.H. Choi, M.L. Minus, S. Kumar, Carbon
nanotube reinforced small di ameter polyacrylonitrile based carbon fiber, Compos. Sci.
Technol. 69 (3–4) (2009) 406–413.)
produce fine PAN-based carbon fibers with diameters down to 500 nm. The
strength of the resulting carbon fiber increases with decreasing fiber diameter
(Fig. 5.9C). The strength of CNT-containing carbon fiber is 30%–60% higher
than control pure PAN-based carbon fiber. The reinforcement efficiency of
CNT becomes higher at a smaller diameter with the effective CNT rein-
forcement stresses of 67, 61, and 28 GPa for carbon fiber diameters of 1, 6, and