Page 101 - Carbon Nanotube Fibres and Yarns
P. 101
Carbon nanotube-reinforced polymer nanocomposite fibers 93
5.4.2 CNT alignment
The alignment of CNTs is critical to the modulus of nanocomposite fibers.
According to continuum mechanics, the effect of SWNT rope orientation
on its reinforcement modulus inside a nanocomposite could be estimated
by the following equation:
1 = 1 cos θ + 1 sin θ + 1 − 2γ 12 sin θ cos θ
4
4
2
2
E x E 1 E 2 G 12 E 1 (5.1)
where E 1 is the longitude modulus and E 2 is the transverse modulus of
CNT ropes, G 12 is the in-plane shear modulus, E x is the reinforcement
modulus of the CNT rope along the axis direction, and θ is the angle
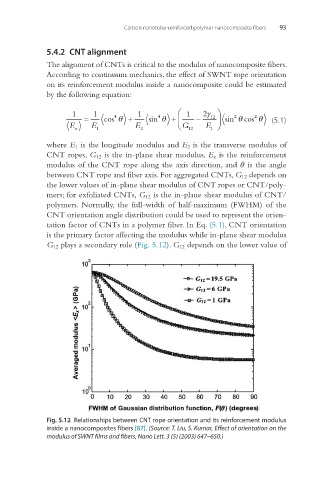
between CNT rope and fiber axis. For aggregated CNTs, G 12 depends on
the lower values of in-plane shear modulus of CNT ropes or CNT/poly-
mers; for exfoliated CNTs, G 12 is the in-plane shear modulus of CNT/
polymers. Normally, the full-width of half-maximum (FWHM) of the
CNT orientation angle distribution could be used to represent the orien-
tation factor of CNTs in a polymer fiber. In Eq. (5.1), CNT orientation
is the primary factor affecting the modulus while in-plane shear modulus
G 12 plays a secondary role (Fig. 5.12). G 12 depends on the lower value of
Fig. 5.12 Relationships between CNT rope orientation and its reinforcement modulus
inside a nanocomposites fibers [87]. (Source: T. Liu, S. Kumar, Effect of orientation on the
modulus of SWNT films and fibers, Nano Lett. 3 (5) (2003) 647–650.)