Page 31 - Carbon Nanotubes
P. 31
22 V. IVANOV et al.
after cooling and reheating the carbon deposited performed on metal-supported catalysts with larger
sample. Metal particles even found near the tips of and, thus, less active metal aggregates.
the tubules were always covered by graphite layers. It is also important to point out that pure cobalt
It supports the model of an “extrusion” of the carbon oxide, alone or finely dispersed in SiO, (i.e. Co-SiO,,
tubules from the surface of active particles [24]. Co-SO,-1 and Co-Si02-2 in Table l), zeolite HY,
3.2.4 Injuence of hydrogen. The influence of fullerene (i.e. C60/C70 : 80/20) is at least as effective
the presence of hydrogen in the reaction mixture on as the reduced oxides for the production of nanotu-
the formation of nanofibres has been shown in various bules in our experimental conditions. In fact, the
papersC1-3, 18, 25, 261. It was postulated that the catalysts studied in this work are also active if the
presence of H2 decreases the rate of hydrocarbon hydrogenation step is not performed. This important
decomposition and as a result favours the process of point, is presently being investigated in our laboratory
carbon polycondensation over the production of fil- in order to elucidate the nature of the active catalyst
aments. However, the addition of hydrogen into the (probably a metal carbide) for the production of
mixture of acetylene and nitrogen did not give major nanotubules.
effects on the tubule formation in our case. We
suppose that the activity of metal nanoparticles on 3.3 The amount of hydrogen injlaments
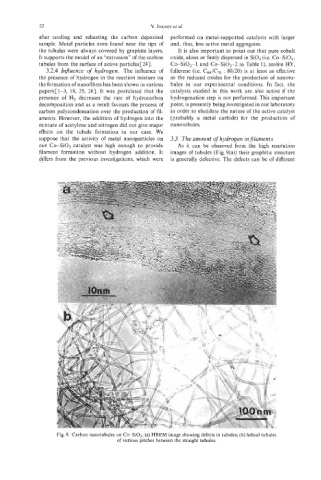
our Co-SiO, catalyst was high enough to provide As it can be observed from the high resolution
filament formation without hydrogen addition. It images of tubules (Fig. 9(a)) their graphitic structure
differs from the previous investigations, which were is generally defective. The defects can be of different
Fig. 9. Carbon nanotubules on Co-SO,: (a) HREM image showing defects in tubules; (b) helical tubules
of various pitches between the straight tubules.