Page 35 - Carbonate Facies in Geologic History
P. 35
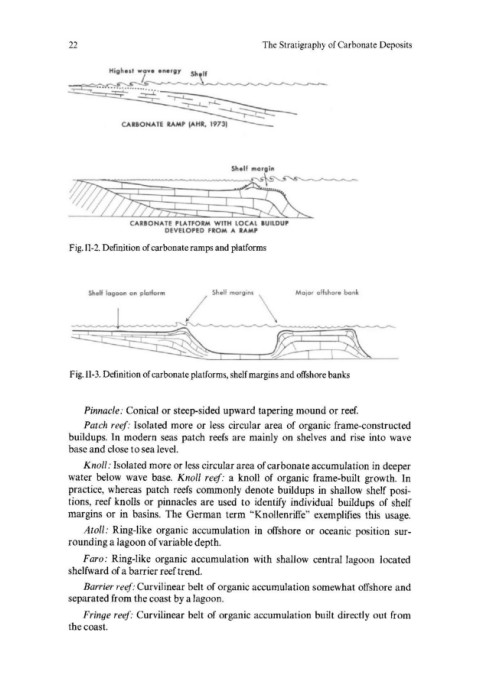
22 The Stratigraphy of Carbonate Deposits
CAR80NATE RAMP IAHR, 1973)
~83,:i~
CARBONATE PLATFORM WITH LOCAL 8UILDUP
DEVELOPED fROM A RAMP
Fig. U-2. Definition of carbonate ramps and platforms
Shell lagoon on platform Shelf morgins MOlor offshore bonk
Fig. U-3. Definition of carbonate platforms, shelf margins and offshore banks
Pinnacle: Conical or steep-sided upward tapering mound or reef.
Patch reef: Isolated more or less circular area of organic frame-constructed
buildups. In modern seas patch reefs are mainly on shelves and rise into wave
base and close to sea level.
Knoll: Isolated more or less circular area of carbonate accumulation in deeper
water below wave base. Knoll reef: a knoll of organic frame-built growth. In
practice, whereas patch reefs commonly denote buildups in shallow shelf posi-
tions, reef knolls or pinnacles are used to identify individual buildups of shelf
margins or in basins. The German term "Knollenriffe" exemplifies this usage.
Atoll: Ring-like organic accumulation in offshore or oceanic position sur-
rounding a lagoon of variable depth.
Faro: Ring-like organic accumulation with shallow central lagoon located
shelfward of a barrier reef trend.
Barrier reef: Curvilinear belt of organic accumulation somewhat offshore and
separated from the coast by a lagoon.
Fringe reef: Curvilinear belt of organic accumulation built directly out from
the coast.