Page 39 - Carbonate Facies in Geologic History
P. 39
26 The Stratigraphy of Carbonate Deposits
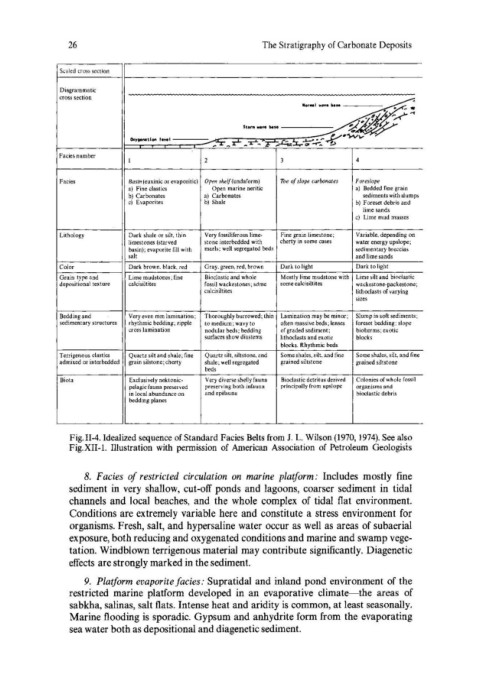
Scaled cross section
Diagrammatic
cross section
~
Ionlll Wfte NH
. " .
.' y .....
~ .
$tOni wwe It ... ~ .'
o.y,..,.tlon I..,.' ...J.--- ,..k''\oovv -
:""r _ r'- _ -r_ ~T";....c:;"!x.-',,,....-:. ~
Facies number
1 2 3 4
Facies Basin (euxinic or evaporitic) Open she!{(undaform) The of slope carbonates Foreslope
a) Fine clastics Open marine neritic a) Bedded fine grain
b) Carbonates a) Carbonates sediments with slumps
c) Evaporites b) Shale b) Foreset debris and
lime sands
c) Lime mud masses
Lithology Dark shale or silt. thin Very fossiliferous Iime- Fine grain limestone; Variable. depending on
limestones (starved stone interbedded with cherty in some cases water energy upslope;
basin); evaporite fill with marls; well segregated beds sedimentary breccias
salt and lime sands
Color Dark brown. black. red Gray. green. red. brown Dark to light Dark to light
Grain type and Lime mudstones; fine Bioclastic and whole Mostly lime mudstone with Lime silt and bioclastic
depositional texture calcisiltites fossil wackestones; sdme some calcisiltites wackestone-packestone;
calcisiltites lithoclasts of varying
sizes
Bedding and Very even mm lamination; Thoroughly burrowed; thin Lamination may be minor; Slump in soft sediments;
sedimentary structures rhythmic bedding; ripple to medium; wavy to often massive beds; lenses foreset bedding; slope
cross lamination nodular beds; bedding of graded sediment; bioherms; exotic
surfaces show diastems lithoclasts and exotic blocks
blocks. Rhythmic beds
Terrigenous clastics Quartz silt and shale; fine Quartz silt. siltstone. and Some shales. silt. and fine Some shales, silt, and fine
admixed or interbedded grain silstone; cherty shale; well segregated grained siltstone grained siltstone
beds
Biota Exclusively nektonic- Very diverse shelly fauna Bioclastic detritus derived Colonies of whole fossil
pelagic fauna preserved preserving both infauna principally from upslope organisms and
in local abundance on and epifauna bioclastic debris
bedding planes
Fig. 11-4. Idealized sequence of Standard Facies Belts from 1. L. Wilson (1970, 1974). See also
Fig.XII-L Illustration with permission of American Association of Petroleum Geologists
8. Facies of restricted circulation on marine platform,' Includes mostly fine
sediment in very shallow, cut-off ponds and lagoons, coarser sediment in tidal
channels and local beaches, and the whole complex of tidal flat environment.
Conditions are extremely variable here and constitute a stress environment for
organisms. Fresh, salt, and hypersaline water occur as well as areas of subaerial
exposure, both reducing and oxygenated conditions and marine and swamp vege-
tation. Windblown terrigenous material may contribute significantly. Diagenetic
effects are strongly marked in the sediment.
9. Platform evaporite Jacies,' Supratidal and inland pond environment of the
restricted marine platform developed in an evaporative climate-the areas of
sabkha, salinas, salt flats. Intense heat and aridity is common, at least seasonally.
Marine flooding is sporadic. Gypsum and anhydrite form from the evaporating
sea water both as depositional and diagenetic sediment.