Page 386 - Carbonate Facies in Geologic History
P. 386
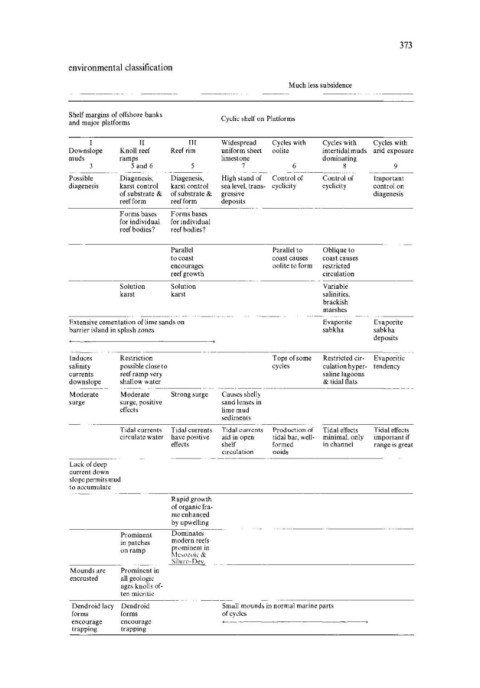
373
environmental classification
Much less subsidence
Shelf margins of offshore banks Cyclic shelf on Platforms
and major platforms
II III Widespread Cycles with Cycles with Cycles with
Downslope Knoll reef Reefrim uniform sheet oolite intertidal muds arid exposure
muds ramps limestone dominating
5 and 6 7 6 8 9
Possible Diagenesis, Diagenesis, High stand of Control of Control of Important
diagenesis karst control karst control sea level, trans- cyclicity cyclicity control on
of substrate & of substrate & gressive diagenesis
reef form reefform deposits
Forms bases Forms bases
for individual for individual
reef bodies? reef bodies?
Parallel Parallel to Oblique to
to coast coast causes coast causes
encourages oolite to form restricted
reef growth circulation
Solution Solution Variable
karst karst salinities,
brackish
marshes
Extensive cementation oflime sands on Evaporite Evaporite
barrier island in splash zones sabkha sabkha
deposits
Induces Restriction Tops of some Restricted cir- Evaporitic
salinity possible close to cycles culation hyper- tendency
currents reef ramp very saline lagoons
downslope shallow water & tidal flats
Moderate Moderate Strong surge Causes shelly
surge surge, positive sand lenses in
effects lime mud
sediments
Tidal currents Tidal currents Tidal curren ts Production of Tidal effects Tidal effects
circulate water have positive aid in open tidal bar, well- minimal, only important if
effects shelf formed in channel range is great
circulation ooids
Lack of deep
current down
slope permits mud
to accumulate
Rapid growth
of organic fra-
me enhanced
by upwelling
Prominent Dominates
in patches modern reefs
on ramp prominent in
Mc,ozoic &
________________________ ~S~iI~lI~r(~)-~D~e~v. ________________________________________________ ___
Mounds are Prominent in
encrusted all geologic
ages knolls of-
ten micritic
Dendroid lacy Dendroid Small mounds in normal marine parts
forms forms of cycles
encourage encourage
trapping trapping