Page 384 - Carbonate Facies in Geologic History
P. 384
Interrelationships of Parameters 371
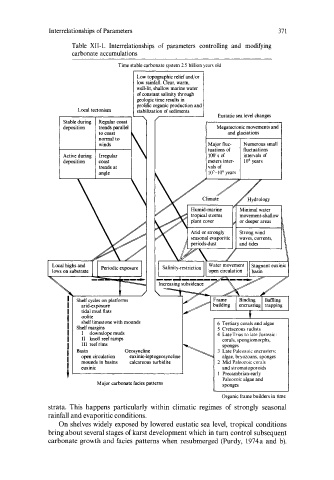
Table XII -1. Interrelationships of parameters controlling and modifying
carbonate accumulations
Time stable carbonate system 2.5 billion years old
Low topographic relief and/or
low rainfall. Clear, warm,
well-lit, shallow marine water
of constant salinity through
geologic time results in
prolific organic production and
Local tectonism stabilization of sediments
Eustatic sea level changes
Stable during Regular coast
deposition trends parallel Megatectonic movements and
to coast and glaciations
normal to
winds Major fluc- Numerous small
tuations of fluctuations
Active during Irregular 100's of intervals of
deposition coast meters inter- 10' years
trends at vals of
angle 10'-10 6 years
Shelf cycles on platforms
arid-exposure
tidal mud flats
oolite
shelf limestone with mounds
Shelf margins
I downslope muds 4 Late Trias to late Jurassic:
II knoll reef ramps corals, spongiomorphs,
III reef rims sponges
Basin Geosyncline 3 Late Paleozoic encrusters:
open circulation euxinic-leptogeosyncline algae, bryozoans, sponges
mounds in basins calcareous turbidite 2 Mid Paleozoic corals
euxinic and stromatoporoids
Precambrian-early
Paleozoic algae and
Major carbonate facies patterns sponges
Organic frame builders in time
strata. This happens particularly within climatic regimes of strongly seasonal
rainfall and evaporitic conditions.
On shelves widely exposed by lowered eustatic sea level, tropical conditions
bring about several stages of karst development which in turn control subsequent
carbonate growth and facies patterns when resubmerged (Purdy, 1974a and b).