Page 46 - Carbonate Sedimentology and Sequence Stratigraphy
P. 46
CHAPTER 2: PRINCIPLES OF CARBONATE PRODUCTION 37
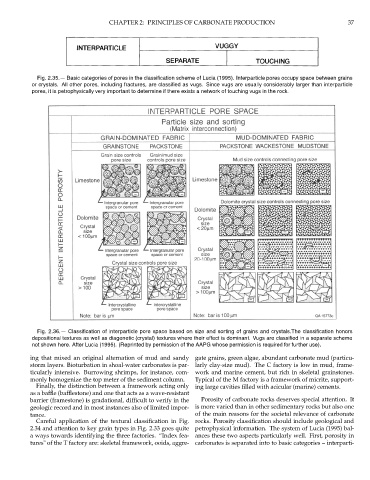
Fig. 2.35.— Basic categories of pores in the classification scheme of Lucia (1995). Interparticle pores occupy space between grains
or crystals. All other pores, including fractures, are classified as vugs. Since vugs are usually considerably larger than interparticle
pores, it is petrophysically very important to determine if there exists a network of touching vugs in the rock.
Fig. 2.36.— Classification of interparticle pore space based on size and sorting of grains and crystals.The classification honors
depositional textures as well as diagenetic (crystal) textures where their effect is dominant. Vugs are classified in a separate scheme
not shown here. After Lucia (1995). (Reprinted by permission of the AAPG whose permission is required for further use).
ing that mixed an original alternation of mud and sandy gate grains, green algae, abundant carbonate mud (particu-
storm layers. Bioturbation in shoal-water carbonates is par- larly clay-size mud). The C factory is low in mud, frame-
ticularly intensive. Burrowing shrimps, for instance, com- work and marine cement, but rich in skeletal grainstones.
monly homogenize the top meter of the sediment column. Typical of the M factory is a framework of micrite, support-
Finally, the distinction between a framework acting only ing large cavities filled with acicular (marine) cements.
as a baffle (bafflestone) and one that acts as a wave-resistant
barrier (framestone) is gradational, difficult to verify in the Porosity of carbonate rocks deserves special attention. It
geologic record and in most instances also of limited impor- is more varied than in other sedimentary rocks but also one
tance. of the main reasons for the societal relevance of carbonate
Careful application of the textural classification in Fig. rocks. Porosity classification should include geological and
2.34 and attention to key grain types in Fig. 2.33 goes quite petrophysical information. The system of Lucia (1995) bal-
a ways towards identifying the three factories. “Index fea- ances these two aspects particularly well. First, porosity in
tures" of the T factory are: skeletal framework, ooids, aggre- carbonates is separated into to basic categories – interparti-