Page 264 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 264
Copolymerization 227
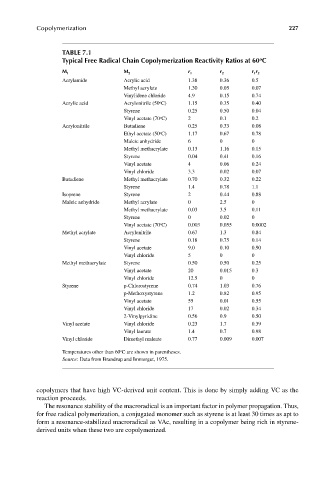
TABLE 7.1
Typical Free Radical Chain Copolymerization Reactivity Ratios at 60 C
o
M 1 M 2 r 1 r 2 r 1 r 2
Acrylamide Acrylic acid 1.38 0.36 0.5
Methyl acrylate 1.30 0.05 0.07
Vinylidene chloride 4.9 0.15 0.74
o
Acrylic acid Acrylonitrile (50 C) 1.15 0.35 0.40
Styrene 0.25 0.50 0.04
o
Vinyl acetate (70 C) 2 0.1 0.2
Acrylonitrile Butadiene 0.25 0.33 0.08
o
Ethyl acetate (50 C) 1.17 0.67 0.78
Maleic anhydride 6 0 0
Methyl methacrylate 0.13 1.16 0.15
Styrene 0.04 0.41 0.16
Vinyl acetate 4 0.06 0.24
Vinyl chloride 3.3 0.02 0.07
Butadiene Methyl methacrylate 0.70 0.32 0.22
Styrene 1.4 0.78 1.1
Isoprene Styrene 2 0.44 0.88
Maleic anhydride Methyl acrylate 0 2.5 0
Methyl methacrylate 0.03 3.5 0.11
Styrene 0 0.02 0
o
Vinyl acetate (70 C) 0.003 0.055 0.0002
Methyl acrylate Acrylonitrile 0.67 1.3 0.84
Styrene 0.18 0.75 0.14
Vinyl acetate 9.0 0.10 0.90
Vinyl chloride 5 0 0
Methyl methacrylate Styrene 0.50 0.50 0.25
Vinyl acetate 20 0.015 0.3
Vinyl chloride 12.5 0 0
Styrene p-Chlorostyrene 0.74 1.03 0.76
p-Methoxystyrene 1.2 0.82 0.95
Vinyl acetate 55 0.01 0.55
Vinyl chloride 17 0.02 0.34
2-Vinylpyridine 0.56 0.9 0.50
Vinyl acetate Vinyl chloride 0.23 1.7 0.39
Vinyl laurate 1.4 0.7 0.98
Vinyl chloride Dimethyl maleate 0.77 0.009 0.007
o
Temperatures other than 60 C are shown in parentheses.
Source: Data from Brandrup and Immergut, 1975.
copolymers that have high VC-derived unit content. This is done by simply adding VC as the
reaction proceeds.
The resonance stability of the macroradical is an important factor in polymer propagation. Thus,
for free radical polymerization, a conjugated monomer such as styrene is at least 30 times as apt to
form a resonance-stabilized macroradical as VAc, resulting in a copolymer being rich in styrene-
derived units when these two are copolymerized.
9/14/2010 3:39:54 PM
K10478.indb 227 9/14/2010 3:39:54 PM
K10478.indb 227