Page 29 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 29
xxviii Polymer Nomenclature
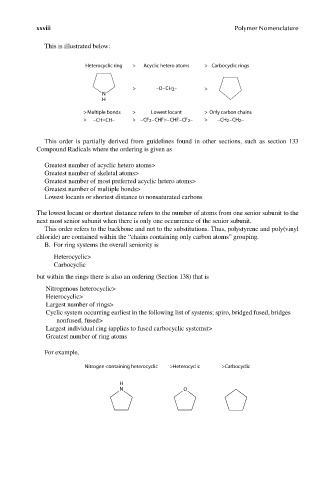
This is illustrated below:
Heterocyclic ring > Acyclic hetero atoms > Carbocyclic rings
> –O – CH2– >
N
H
>Multiple bonds > Lowest locant > Only carbon chains
> –CH=CH– > – CF2 – CHF>– CHF – CF2– > – CH2 – CH2–
This order is partially derived from guidelines found in other sections, such as section 133
Compound Radicals where the ordering is given as
Greatest number of acyclic hetero atoms>
Greatest number of skeletal atoms>
Greatest number of most preferred acyclic hetero atoms>
Greatest number of multiple bonds>
Lowest locants or shortest distance to nonsaturated carbons
The lowest locant or shortest distance refers to the number of atoms from one senior subunit to the
next most senior subunit when there is only one occurrence of the senior subunit.
This order refers to the backbone and not to the substitutions. Thus, polystyrene and poly(vinyl
chloride) are contained within the “chains containing only carbon atoms” grouping.
B. For ring systems the overall seniority is
Heterocyclic>
Carbocyclic
but within the rings there is also an ordering (Section 138) that is
Nitrogenous heterocyclic>
Heterocyclic>
Largest number of rings>
Cyclic system occurring earliest in the following list of systems; spiro, bridged fused, bridges
nonfused, fused>
Largest individual ring (applies to fused carbocyclic systems)>
Greatest number of ring atoms
For example,
Nitrogen-containing heterocyclic >Heterocyclic >Carbocyclic
H
N O
9/14/2010 3:35:46 PM
K10478.indb xxviii 9/14/2010 3:35:46 PM
K10478.indb xxviii