Page 318 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 318
Naturally Occurring Polymers—Plants 281
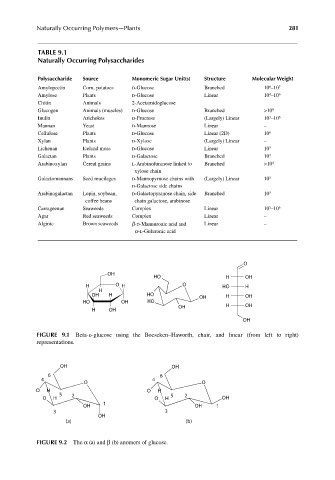
TABLE 9.1
Naturally Occurring Polysaccharides
Polysaccharide Source Monomeric Sugar Unit(s) Structure Molecular Weight
6
Amylopectin Corn, potatoes d-Glucose Branched 10 –10 7
Amylose Plants d-Glucose Linear 10 –10 6
4
Chitin Animals 2-Acetamidoglucose
Glucogen Animals (muscles) d-Glucose Branched >10 8
Inulin Arichokes d-Fructose (Largely) Linear 10 –10 6
3
Mannan Yeast d-Mannose Linear –
Cellulose Plants d-Glucose Linear (2D) 10 6
Xylan Plants d-Xylose (Largely) Linear –
Lichenan Iceland moss d-Glucose Linear 10 5
Galactan Plants d-Galactose Branched 10 4
Arabinoxylan Cereal grains l-Arabinofuranose linked to Branched >10 4
xylose chain
Galactomannans Seed mucilages d-Mannopyrnose chains with (Largely) Linear 10 5
d-Galactose side chains
Arabinogalactan Lupin, soybean, d-Galactopyranose chain, side Branched 10 5
coffee beans chain galactose, arabinose
Carrageenan Seaweeds Complex Linear 10 –10 6
5
Agar Red seaweeds Complex Linear –
Alginic Brown seaweeds β-d-Mannuronic acid and Linear –
α-l-Guluronic acid
O
OH
HO H OH
H O H O HO H
H
OH H HO
OH H OH
HO OH HO
OH H OH
H OH
OH
FIGURE 9.1 Beta-d-glucose using the Boeseken–Haworth, chair, and linear (from left to right)
representations.
OH OH
6 6
4 4
O O
O H O H
5 2 5 2
O H O H OH
OH 1 OH 1
3 3
OH
(a) (b)
FIGURE 9.2 The α (a) and β (b) anomers of glucose.
9/14/2010 3:40:37 PM
K10478.indb 281 9/14/2010 3:40:37 PM
K10478.indb 281