Page 337 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 337
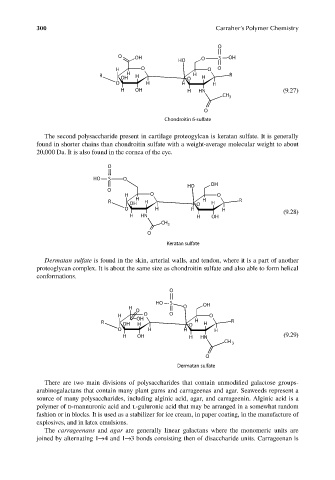
300 Carraher’s Polymer Chemistry
O
O OH S OH
HO O
H O O O
R H H H R
OH O H
O H H H
H OH H HN (9.27)
CH 3
O
Chondroitin 6-sulfate
The second polysaccharide present in cartilage proteogylcan is keratan sulfate. It is generally
found in shorter chains than chondroitin sulfate with a weight-average molecular weight to about
20,000 Da. It is also found in the cornea of the eye.
O
HO S O
HO OH
O
H O O
H
R OH H O H H R
O H H H (9.28)
H HN H OH
CH 3
O
Keratan sulfate
Dermatan sulfate is found in the skin, arterial walls, and tendon, where it is a part of another
proteoglycan complex. It is about the same size as chondroitin sulfate and also able to form helical
conformations.
O
HO S OH
H O
O
H O O O
R OH OH O H H R
H
O H H H
H OH H HN (9.29)
CH 3
O
Dermatan sulfate
There are two main divisions of polysaccharides that contain unmodified galactose groups-
arabinogalactans that contain many plant gums and carrageenas and agar. Seaweeds represent a
source of many polysaccharides, including alginic acid, agar, and carrageenin. Alginic acid is a
polymer of d-mannuronic acid and l-guluronic acid that may be arranged in a somewhat random
fashion or in blocks. It is used as a stabilizer for ice cream, in paper coating, in the manufacture of
explosives, and in latex emulsions.
The carrageenans and agar are generally linear galactans where the monomeric units are
joined by alternating 1→4 and 1→3 bonds consisting then of disaccharide units. Carrageenan is
9/14/2010 3:40:48 PM
K10478.indb 300
K10478.indb 300 9/14/2010 3:40:48 PM