Page 336 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 336
Naturally Occurring Polymers—Plants 299
9.8 HETEROPOLYSACCHARIDES
Heteropolysaccharides contain two or more different monosaccharides. Glycosaminoglycans are
polysaccharides that contain aminosugar units. Most are of animal origin.
Above is a representative structure of heparin (9.24) that is complex containing d-glucuronic acid,
l-iduronic acid, and d-glucosamine units. The glucosamine units may be n-acetylated or n-sulfonated.
It is found in the lung, liver, and arterial walls of mammals. It is also found in intracellular granules of
mast cells that line arterial walls and is released through injury. The glucuronic acid and iduronic acid
units are not randomly present but occur in blocks. Heparin is found as the free polysaccharide and
bonded to protein. Heparin acts as an anticoagulant, an inhibitor of blood clotting, and is widely used
for this in medicine. In nature its purpose appears to be to prevent uncontrolled clotting.
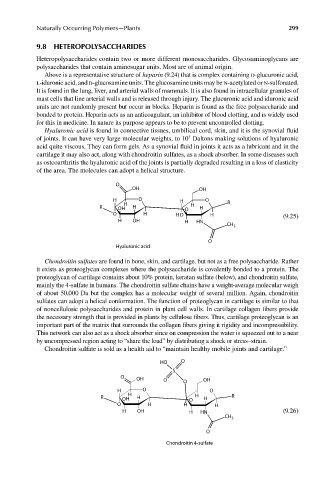
Hyaluronic acid is found in connective tissues, umbilical cord, skin, and it is the synovial fl uid
7
of joints. It can have very large molecular weights, to 10 Daltons making solutions of hyaluronic
acid quite viscous. They can form gels. As a synovial fluid in joints it acts as a lubricant and in the
cartilage it may also act, along with chondroitin sulfates, as a shock absorber. In some diseases such
as osteoarthritis the hyaluronic acid of the joints is partially degraded resulting in a loss of elasticity
of the area. The molecules can adopt a helical structure.
O
OH OH
H O H O R
H H
R OH H O H
O H H O H (9.25)
H OH H HN
CH 3
O
Hyaluronic acid
Chondroitin sulfates are found in bone, skin, and cartilage, but not as a free polysaccharide. Rather
it exists as proteoglycan complexes where the polysaccharide is covalently bonded to a protein. The
proteoglycan of cartilage contains about 10% protein, keratan sulfate (below), and chondroitin sulfate,
mainly the 4-sulfate in humans. The chondroitin sulfate chains have a weight-average molecular weigh
of about 50,000 Da but the complex has a molecular weight of several million. Again, chondroitin
sulfates can adopt a helical conformation. The function of proteoglycan in cartilage is similar to that
of noncellulosic polysaccharides and protein in plant cell walls. In cartilage collagen fi bers provide
the necessary strength that is provided in plants by cellulose fi bers. Thus, cartilage proteoglycan is an
important part of the matrix that surrounds the collagen fi bers giving it rigidity and incompressibility.
This network can also act as a shock absorber since on compression the water is squeezed out to a near
by uncompressed region acting to “share the load” by distributing a shock or stress–strain.
Chondroitin sulfate is sold as a health aid to “maintain healthy mobile joints and cartilage.”
HO O
S
O OH O O OH
H O O
R OH H H O H H R
O H H H
H OH H HN (9.26)
CH 3
O
Chondroitin 4-sulfate
9/14/2010 3:40:47 PM
K10478.indb 299 9/14/2010 3:40:47 PM
K10478.indb 299