Page 449 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 449
412 Carraher’s Polymer Chemistry
are used, after treatment with sulfuric acid, to create acidic surface sites, as petroleum cracking
catalysts. Asbestos also has a layered structure (Section 12.13).
12.4.3 CHAIN
Both single- and double-stranded chains are found. The most important members of single chains
are the pyroxenes and include diopside. The most important double-chained minerals are the amphi-
boles. Some of these contain hydroxyl and fluoride ions, bonded directly to the metal cation and not
to the silicon atom.
Jade, which has been valued in carving by eastern Asians for centuries, is generally one of two
+2
+2
minerals—pyroxene or jadeite, NaAl(SiO ) , and the amphibole nephrite, Ca (Fe and/or Mg )
3 2 2 5
(Si O ) (OH) . X-Ray diffraction has shown the presence of triple chains in nephrite.
4 11 2 2
Because the interchain bonding is weaker them the Si-O backbone bonding, these chain struc-
tures can generally be easily cleaved between the chains.
Several amphiboles are fibrous and fibers from them can be processed to give heat-insulating
materials. Among these are tremolite and crocidolite. These minerals are also used as fi bers in
composites.
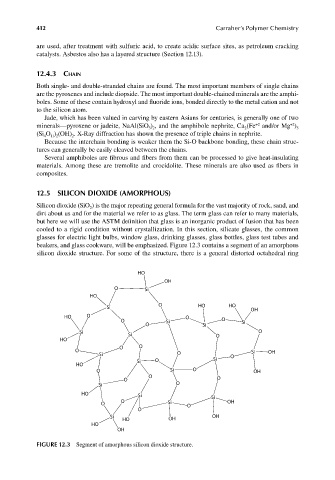
12.5 SILICON DIOXIDE (AMORPHOUS)
Silicon dioxide (SiO ) is the major repeating general formula for the vast majority of rock, sand, and
2
dirt about us and for the material we refer to as glass. The term glass can refer to many materials,
but here we will use the ASTM definition that glass is an inorganic product of fusion that has been
cooled to a rigid condition without crystallization. In this section, silicate glasses, the common
glasses for electric light bulbs, window glass, drinking glasses, glass bottles, glass test tubes and
beakers, and glass cookware, will be emphasized. Figure 12.3 contains a segment of an amorphous
silicon dioxide structure. For some of the structure, there is a general distorted octahedral ring
HO
OH
O Si
HO
O HO HO
Si
OH
HO O O
O Si O Si
O Si
Si O
Si O
HO
O O
O Si OH
Si O O
Si O Si
HO
O Si O OH
O O
O
Si O
HO Si Si
O OH
O Si O
O
Si OH
HO OH
HO
OH
FIGURE 12.3 Segment of amorphous silicon dioxide structure.
9/14/2010 3:42:01 PM
K10478.indb 412 9/14/2010 3:42:01 PM
K10478.indb 412