Page 499 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 499
462 Carraher’s Polymer Chemistry
Exothermic
T g
T
Endothermic m
Temperature
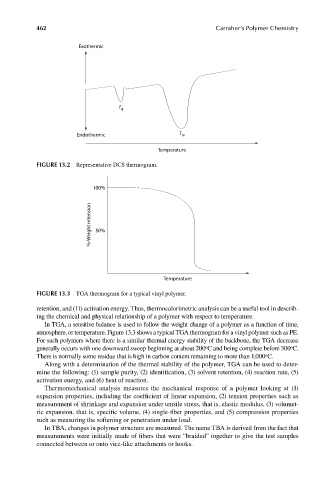
FIGURE 13.2 Representative DCS thermogram.
100%
%-Weight retension 50%
Temperature
FIGURE 13.3 TGA thermogram for a typical vinyl polymer.
retention, and (11) activation energy. Thus, thermocalorimetric analysis can be a useful tool in describ-
ing the chemical and physical relationship of a polymer with respect to temperature.
In TGA, a sensitive balance is used to follow the weight change of a polymer as a function of time,
atmosphere, or temperature. Figure 13.3 shows a typical TGA thermogram for a vinyl polymer such as PE.
For such polymers where there is a similar thermal energy stability of the backbone, the TGA decrease
generally occurs with one downward sweep beginning at about 200 C and being complete before 300 C.
o
o
There is normally some residue that is high in carbon content remaining to more than 1,000 C.
o
Along with a determination of the thermal stability of the polymer, TGA can be used to deter-
mine the following: (1) sample purity, (2) identification, (3) solvent retention, (4) reaction rate, (5)
activation energy, and (6) heat of reaction.
Thermomechanical analysis measures the mechanical response of a polymer looking at (1)
expansion properties, including the coefficient of linear expansion, (2) tension properties such as
measurement of shrinkage and expansion under tensile stress, that is, elastic modulus, (3) volumet-
ric expansion, that is, specific volume, (4) single-fiber properties, and (5) compression properties
such as measuring the softening or penetration under load.
In TBA, changes in polymer structure are measured. The name TBA is derived from the fact that
measurements were initially made of fibers that were “braided” together to give the test samples
connected between or onto vice-like attachments or hooks.
9/14/2010 3:42:15 PM
K10478.indb 462 9/14/2010 3:42:15 PM
K10478.indb 462