Page 576 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 576
Reactions on Polymers 539
OH
O OH
+
Receptor site
O
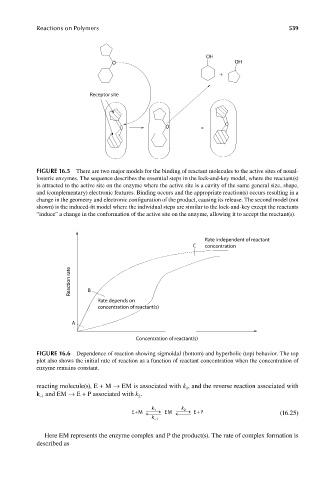
FIGURE 16.5 There are two major models for the binding of reactant molecules to the active sites of nonal-
losteric enzymes. The sequence describes the essential steps in the lock-and-key model, where the reactant(s)
is attracted to the active site on the enzyme where the active site is a cavity of the same general size, shape,
and (complementary) electronic features. Binding occurs and the appropriate reaction(s) occurs resulting in a
change in the geometry and electronic configuration of the product, causing its release. The second model (not
shown) is the induced-fit model where the individual steps are similar to the lock-and-key except the reactants
“induce” a change in the conformation of the active site on the enzyme, allowing it to accept the reactant(s).
Rate independent of reactant
C concentration
Reaction rate B
Rate depends on
concentration of reactant(s)
A
Concentration of reactant(s)
FIGURE 16.6 Dependence of reaction showing sigmoidal (bottom) and hyperbolic (top) behavior. The top
plot also shows the initial rate of reaction as a function of reactant concentration when the concentration of
enzyme remains constant.
reacting molecule(s), E + M → EM is associated with k , and the reverse reaction associated with
1
k and EM → E + P associated with k .
2
−1
k k
E + M 1 EM 2 E + P (16.25)
k
−1
Here EM represents the enzyme complex and P the product(s). The rate of complex formation is
described as
9/14/2010 3:43:10 PM
K10478.indb 539 9/14/2010 3:43:10 PM
K10478.indb 539