Page 677 - Carrahers_Polymer_Chemistry,_Eighth_Edition
P. 677
640 Carraher’s Polymer Chemistry
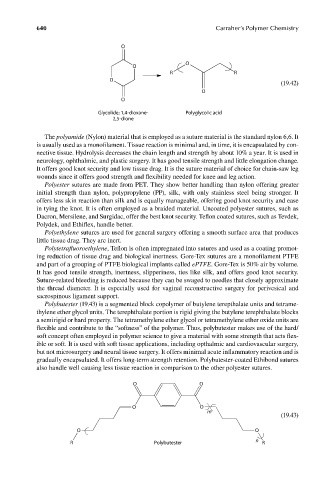
O
O
O
R R
O
(19.42)
O
O
Glycolide; 1,4-dioxane- Polyglycolic acid
2,5-dione
The polyamide (Nylon) material that is employed as a suture material is the standard nylon 6,6. It
is usually used as a monofilament. Tissue reaction is minimal and, in time, it is encapsulated by con-
nective tissue. Hydrolysis decreases the chain length and strength by about 10% a year. It is used in
neurology, ophthalmic, and plastic surgery. It has good tensile strength and little elongation change.
It offers good knot security and low tissue drag. It is the suture material of choice for chain-saw leg
wounds since it offers good strength and flexibility needed for knee and leg action.
Polyester sutures are made from PET. They show better handling than nylon offering greater
initial strength than nylon, polypropylene (PP), silk, with only stainless steel being stronger. It
offers less skin reaction than silk and is equally manageable, offering good knot security and ease
in tying the knot. It is often employed as a braided material. Uncoated polyester sutures, such as
Dacron, Mersilene, and Surgidac, offer the best knot security. Teflon coated sutures, such as Tevdek,
Polydek, and Ethiflex, handle better.
Polyethylene sutures are used for general surgery offering a smooth surface area that produces
little tissue drag. They are inert.
Polytetrafl uoroethylene, Tefl on is often impregnated into sutures and used as a coating promot-
ing reduction of tissue drag and biological inertness. Gore-Tex sutures are a monofi lament PTFE
and part of a grouping of PTFE biological implants called ePTFE. Gore-Tex is 50% air by volume.
It has good tensile strength, inertness, slipperiness, ties like silk, and offers good knot security.
Suture-related bleeding is reduced because they can be swaged to needles that closely approximate
the thread diameter. It is especially used for vaginal reconstructive surgery for perivesical and
sacrospinous ligament support.
Polybutester (19.43) is a segmented block copolymer of butylene terepthalate units and tetrame-
thylene ether glycol units. The terephthalate portion is rigid giving the butylene terephthalate blocks
a semirigid or hard property. The tetramethylene ether glycol or tetramethylene ether oxide units are
fl exible and contribute to the “softness” of the polymer. Thus, polybutester makes use of the hard/
soft concept often employed in polymer science to give a material with some strength that acts fl ex-
ible or soft. It is used with soft tissue applications, including opthalmic and cardiovascular surgery,
but not microsurgery and neural tissue surgery. It offers minimal acute inflammatory reaction and is
gradually encapsulated. It offers long-term strength retention. Polybutester-coated Ethibond sutures
also handle well causing less tissue reaction in comparison to the other polyester sutures.
O O
O O
m
(19.43)
O O
n
R Polybutester R
9/14/2010 3:44:03 PM
K10478.indb 640
K10478.indb 640 9/14/2010 3:44:03 PM