Page 26 - Challenges in Corrosion Costs Causes Consequences and Control(2015)
P. 26
4 INTRODUCTION AND FORMS OF CORROSION
Noble (+)
Observed polarization plot
Corrosion
2+
M
M + 2e
current density Anodic branch
Electrode potential vs SCE (V) Tafel slope β a Electrode potential versus SHE (V)
Open-circuit potential
+
H 2 (g)
2H + 2e
Cathodic branch
Tafel slope β c
(–) Active
2
Log current density (mA/cm )
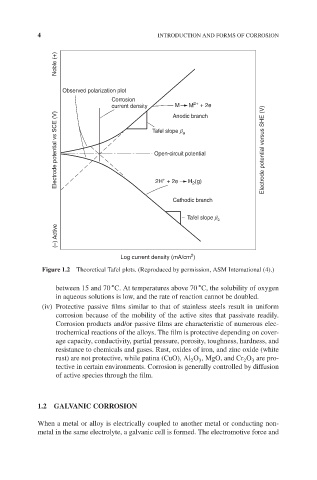
Figure 1.2 Theoretical Tafel plots. (Reproduced by permission, ASM International (4).)
∘ ∘
between 15 and 70 C. At temperatures above 70 C, the solubility of oxygen
in aqueous solutions is low, and the rate of reaction cannot be doubled.
(iv) Protective passive films similar to that of stainless steels result in uniform
corrosion because of the mobility of the active sites that passivate readily.
Corrosion products and/or passive films are characteristic of numerous elec-
trochemical reactions of the alloys. The film is protective depending on cover-
age capacity, conductivity, partial pressure, porosity, toughness, hardness, and
resistance to chemicals and gases. Rust, oxides of iron, and zinc oxide (white
rust) are not protective, while patina (CuO), Al O , MgO, and Cr O are pro-
2
3
2
3
tective in certain environments. Corrosion is generally controlled by diffusion
of active species through the film.
1.2 GALVANIC CORROSION
When a metal or alloy is electrically coupled to another metal or conducting non-
metal in the same electrolyte, a galvanic cell is formed. The electromotive force and