Page 289 - Challenges in Corrosion Costs Causes Consequences and Control(2015)
P. 289
DRINKING WATER AND SEWER SYSTEMS 267
on different materials is complex (44). The rather stringent limits concerning lead
and copper and other ions in drinking water limit the use of inhibitors for corrosion
control.
Corrosion inhibitors for water treatment consist of naturally occurring inhibitors.
Natural inhibitors consist of naturally occurring organic compounds, dissolved silica,
and phosphate. Corrosion protection of iron, zinc coatings, lead, and copper can be
achieved by using naturally occurring inhibitors. The added inhibitors in small quanti-
ties produce a passivating film at anodic sites to suppress the anodic corrosion reaction
or inhibit the cathodic reaction and leading to a decrease in the corrosion rate. Some
of the added inhibitors are orthophosphates, molecularly dehydrated polyphosphates,
bimetallic (zinc-containing) phosphates, silicates, and phosphate-silicate mixtures.
Selection of corrosion inhibitors is a complex task that depends on many factors.
The cost effectiveness of the inhibitor may be obtained from the relationship:
Cost effectiveness = Relative effectiveness × dosage × price per weight. The
inhibitor dosage rate depends on the local water conditions and temporal factors,
such as the time of the year. It should be quantified in terms of percent corrosion
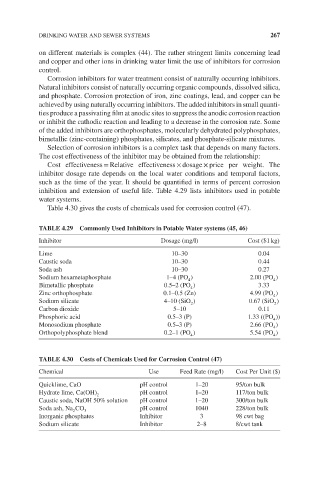
inhibition and extension of useful life. Table 4.29 lists inhibitors used in potable
water systems.
Table 4.30 gives the costs of chemicals used for corrosion control (47).
TABLE 4.29 Commonly Used Inhibitors in Potable Water systems (45, 46)
Inhibitor Dosage (mg/l) Cost ($1 kg)
Lime 10–30 0.04
Caustic soda 10–30 0.44
Soda ash 10–30 0.27
Sodium hexametaphosphate 1–4 (PO ) 2.00 (PO )
4
4
Bimetallic phosphate 0.5–2 (PO ) 3.33
4
Zinc orthophosphate 0.1–0.5 (Zn) 4.99 (PO )
4
Sodium silicate 4–10 (SiO ) 0.67 (SiO )
2 2
Carbon dioxide 5–10 0.11
Phosphoric acid 0.5–3 (P) 1.33 ((PO ))
4
Monosodium phosphate 0.5–3 (P) 2.66 (PO )
4
Orthopolyphosphate blend 0.2–1 (PO ) 5.54 (PO )
4 4
TABLE 4.30 Costs of Chemicals Used for Corrosion Control (47)
Chemical Use Feed Rate (mg/l) Cost Per Unit ($)
Quicklime, CaO pH control 1–20 95/ton bulk
Hydrate lime, Ca(OH) pH control 1–20 117/ton bulk
2
Caustic soda, NaOH 50% solution pH control 1–20 300/ton bulk
Soda ash, Na CO pH control 1040 228/ton bulk
2 3
Inorganic phosphates Inhibitor 3 98 cwt bag
Sodium silicate Inhibitor 2–8 8/cwt tank