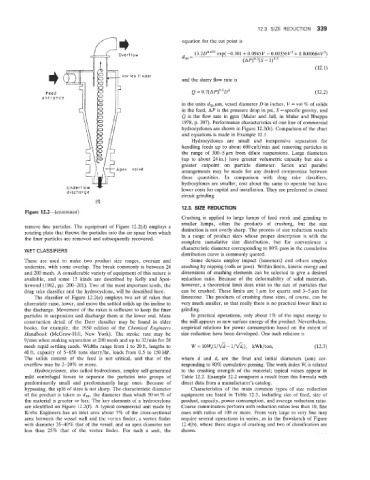
Page 376 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 376
Q* equation for the cut point is 12.3. SIZE REDUCTION 339
Ove
f
ow
I
r
d5, = 13.20°.675 exp(-0.301+ 0.0945V - 0.00356V2 + 0.0000684V3)
(AP)0.3(S - l)0.5
(12.1)
finder
and the slurry flow rate is
Q = 0.7(AP)0.5D2 (12.2)
in the units d,, pm, vessel diameter D in inches, V = vol % of solids
in the feed, AP is the pressure drop in psi, S = specific gravity, and
Q is the flow rate in gpm (Mular and Jull, in Mular and Bhappu
1978, p. 397). Performance characteristics of one line of commercial
hydrocyclones are shown in Figure 12.3(b). Comparison of the chart
and equations is made in Example 12.1.
Hydrocyclones are small and inexpensive separators for
handling feeds up to about 600 cuft/min and removing particles in
the range of 300-5pm from dilute suspensions. Large diameters
(up to about 24in.) have greater volumetric capacity but also a
greater cutpoint on particle diameter. Series and parallel
arrangements may be made for any desired compromise between
these quantities. In comparison with drag rake classifiers,
hydrocylones are smaller, cost about the same to operate but have
lower costs for capital and installation. They are preferred in closed
discharge
circuit grinding.
(B
12.3. SIZE REDUCTION
Crushing is applied to large lumps of feed stock and grinding to
smaller lumps, often the products of crushing, but the size
remove fine particles. The equipment of Figure 12.2(d) employs a
rotating plate that throws the particles into the air space from which distinction is not overly sharp. The process of size reduction results
the finer particles are removed and subsequently recovered. in a range of product sizes whose proper description is with the
complete cumulative size distribution, but for convenience a
WET CLASSIFIERS characteristic diameter corresponding to 80% pass in the cumulative
distribution curve is commonly quoted.
These are used to make two product size ranges, oversize and Some devices employ impact (hammers) and others employ
undersize, with some overlap. The break commonly is between 28 crushing by nipping (rolls or jaws). Within limits, kinetic energy and
and 200 mesh. A considerable variety of equipment of this nature is dimensions of crushing elements can be selected to give a desired
available, and some 1.5 kinds are described by Kelly and Spot- reduction ratio. Because of the deformability of solid materials,
tiswood (1982, pp. 200-201). Two of the most important kinds, the however, a theoretical limit does exist to the size of particles that
drag rake classifier and 1.he hydrocyclone, will be described here. can be crushed. These limits are 1 ym for quartz and 3-5 pm for
The classifier of Figure 12.2(e) employs two set of rakes that limestone. The products of crushing these sizes, of course, can be
alternately raise, :lower, and move the settled solids up the incline to very much smaller, so that really there is no practical lower limit to
the discharge. Movement of the rakes is sufficient to keep the finer grinding.
particles in suspension and discharge them at the lower end. More In practical operations, only about 1% of the input energy to
construction detail of the Dorr classifier may be found in older the mill appears as new surface energy of the product. Nevertheless,
books, for example, the 1950 edition of the Chemical Engineers empirical relations for power consumption based on the extent of
Handbook (McGraw-Hili, New York). The stroke rate may be size reduction have been developed. One such relation is
9/min when making separation at 200 mesh and up to 32/min for 28
mesh rapid settling sandis. Widths range from 1 to 20ft, lengths to W = lOR.(l/~- 1/aZ), kWh/ton, (12.3)
40ft, capacity of 5-850 tons slurry/hr, loads from 0.5 to 150HP.
The solids content of the feed is not critical, and that of the where d and di are the final and initial diameters (ym) cor-
overflow may be 2-20% or more. responding to 80% cumulative passing. The work index is related
Hydrocyclones, also called hydroclones, employ self-generated to the crushing strength of the material; typical values appear in
mild centrifugal forces to separate the particles into groups of Table 12.2. Example 12.2 compares a result from this formula with
predominantly small and predominantly Large ones. Because of direct data from a manufacturer’s catalog.
bypassing, the split of sizes is not sharp. The characteristic diameter Characteristics of the main common types of size reduction
of the product is taken as d,,, the diameter than which 50 wt % of equipment are listed in Table 12.3, including size of feed, size of
the material is greater or less. The key elements of a hydrocyclone product, capacity, power consumption, and average reduction ratio.
are identified on Figure 12.2(f). A typical commercial unit made by Coarse comminuters perform with reduction ratios less than 10, fine
Krebs Engineers has an inlet area about 7(% of the cross-sectional ones with ratios of 100 or more. From very large to very fine may
area between the vessel wall and the vortex finder, a vortex finder require several operations in series, as in the Aowsketch of Figure
with diameter 3540% that of the vessel, and an apex diameter not 12.4(b), where three stages of crushing and two of classification are
less than 25% that of the vortex finder. For such a unit, the shown.