Page 377 - Chemical Process Equipment - Selection and Design
P. 377
340 DISINTEGRATION, AGGLOMERATION, AND SIZE SEPARATION OF PARTICULATE SOLIDS
I I I 1 I
MATtRlAL CURVL MATWAL CUlVl
Carborundum 2 Gravel 2
Cinders 5 Gypsum 3
Cement Cllnker 2 Iron Ore 1
Coal 3 Limestone, Sizing 2
Coke, Siring 6 Limestone. SEalping 1
Breeze Removal 2 Phosphate Rock 3
Copper Ore I Sand.8ank 3
Dolomnte 2 Sand. Foundry 3
Feldspar 3 Slag
Fertduer 4 Slone, Crushed 2
Fluorspar 3
00 0 0
25-65pm a-Ioopm 60-120 /.LIT 100- 200pm
35-75pm 50-110pm 70-150 pm 150-250pm mnge
I
I I I I11111 I I I 1 1 1 1 1 1 I I I 1 1 1 1 1 1
10 20 30 405060( \\W 200 m400500\ \ 1ooo 200030001 6030 \loo00
70 80 90 600 800 4000 8ooo
Cydone copodty-US GPM, (I US GPM = 2221 m3 h-l)
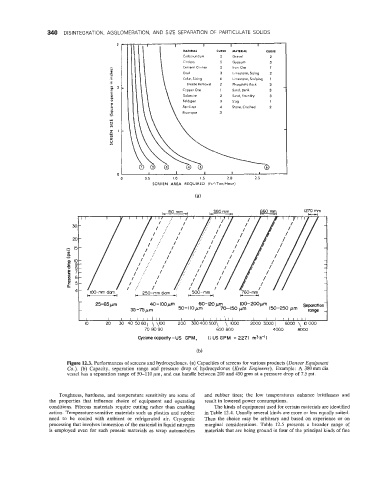
Figure 12.3. Performances of screens and hydrocyclones. (a) Capacities of screens for various products (Denver Equipment
Co.). (b) Capacity, separation range and pressure drop of hydrocyclones (Krebs Engineers). Example: A 380 mm dia
vessel has a separation range of 50-110 pm, and can handle between 200 and 450 gpm at a pressure drop of 7.5 psi.
Toughness, hardness, and temperature sensitivity are some of and rubber tires; the low temperatures enhance brittleness and
the properties that influence choice of equipment and operating result in lowered power consumptions.
conditions. Fibrous materials require cutting rather than crushing The kinds of equipment used for certain materials are identified
action. Temperature-sensitive materials such as plastics and rubber in Table 12.4. Usually several kinds are more or less equally suited.
need to be cooled with ambient or refrigerated air. Cryogenic Then the choice may be arbitrary and based on experience or on
processing that involves immersion of the material in liquid nitrogen marginal considerations. Table 12.5 presents a broader range of
is employed even for such prosaic materials as scrap automobiles materials that are being ground in four of the principal kinds of fine