Page 28 - Chemical and process design handbook
P. 28
Speight_Part 1_C&D 11/7/01 3:03 PM Page 1.14
DEHYDROGENATION
Dehydrogenation is a reaction that results in the removal of hydrogen
from an organic compound or compounds, as in the dehydrogenation of
ethane to ethylene:
CH CH → CH =CH + H
3 3 2 2 2
This process is brought about in several ways. The most common method
is to heat hydrocarbons to high temperature, as in thermal cracking, that
causes some dehydrogenation, indicated by the presence of unsaturated
compounds and free hydrogen.
In the chemical process industries, nickel, cobalt, platinum, palladium,
and mixtures containing potassium, chromium, copper, aluminum, and
other metals are used in very large-scale dehydrogenation processes.
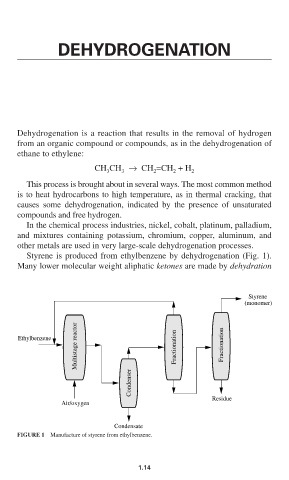
Styrene is produced from ethylbenzene by dehydrogenation (Fig. 1).
Many lower molecular weight aliphatic ketones are made by dehydration
Styrene
(monomer)
Multistage reactor Fractionation Fractionation
Ethylbenzene
Condenser
Residue
Air/oxygen
Condensate
FIGURE 1 Manufacture of styrene from ethylbenzene.
1.14