Page 84 - Chemical and process design handbook
P. 84
Speight_Part II_A 11/7/01 3:16 PM Page 2.25
ACRYLIC ACID
o
o
Acrylic acid (CH =CHCO H, melting point: 13.5 C, boiling point: 141 C,
2 2
o
density: 1.045, flash point: 68 C) and acrylates were once prepared by
reaction of acetylene and carbon monoxide with water or an alcohol, with
nickel carbonyl as catalyst.
HC≡CH + CO + H O → CH =CHCO H
2 2 2
In the presence of such catalysts as a solution of cuprous and ammo-
nium chlorides, hydrogen cyanide adds to acetylene to give acrylonitrile
(CH =CHCN). However, this process has been replaced by processes
2
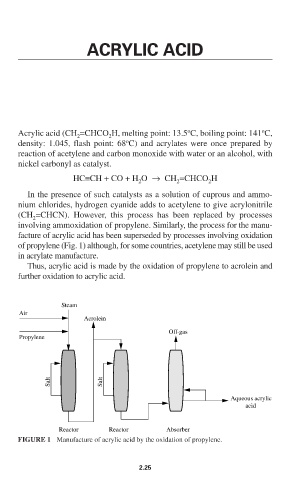
involving ammoxidation of propylene. Similarly, the process for the manu-
facture of acrylic acid has been superseded by processes involving oxidation
of propylene (Fig. 1) although, for some countries, acetylene may still be used
in acrylate manufacture.
Thus, acrylic acid is made by the oxidation of propylene to acrolein and
further oxidation to acrylic acid.
Steam
Air
Acrolein
Off-gas
Propylene
Salt Salt
Aqueous acrylic
acid
Reactor Reactor Absorber
FIGURE 1 Manufacture of acrylic acid by the oxidation of propylene.
2.25