Page 238 - Chemical engineering design
P. 238
214
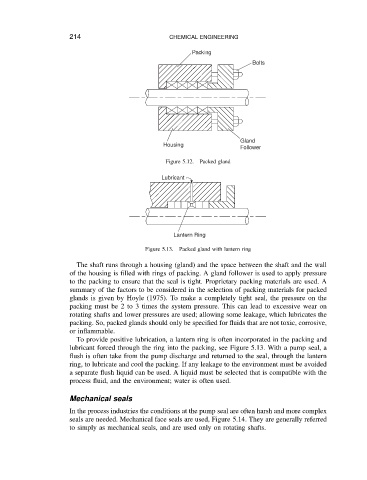
Packing
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING Bolts
Housing Gland
Follower
Figure 5.12. Packed gland
Lubricant
Lantern Ring
Figure 5.13. Packed gland with lantern ring
The shaft runs through a housing (gland) and the space between the shaft and the wall
of the housing is filled with rings of packing. A gland follower is used to apply pressure
to the packing to ensure that the seal is tight. Proprietary packing materials are used. A
summary of the factors to be considered in the selection of packing materials for packed
glands is given by Hoyle (1975). To make a completely tight seal, the pressure on the
packing must be 2 to 3 times the system pressure. This can lead to excessive wear on
rotating shafts and lower pressures are used; allowing some leakage, which lubricates the
packing. So, packed glands should only be specified for fluids that are not toxic, corrosive,
or inflammable.
To provide positive lubrication, a lantern ring is often incorporated in the packing and
lubricant forced through the ring into the packing, see Figure 5.13. With a pump seal, a
flush is often take from the pump discharge and returned to the seal, through the lantern
ring, to lubricate and cool the packing. If any leakage to the environment must be avoided
a separate flush liquid can be used. A liquid must be selected that is compatible with the
process fluid, and the environment; water is often used.
Mechanical seals
In the process industries the conditions at the pump seal are often harsh and more complex
seals are needed. Mechanical face seals are used, Figure 5.14. They are generally referred
to simply as mechanical seals, and are used only on rotating shafts.