Page 319 - Chemical engineering design
P. 319
294
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
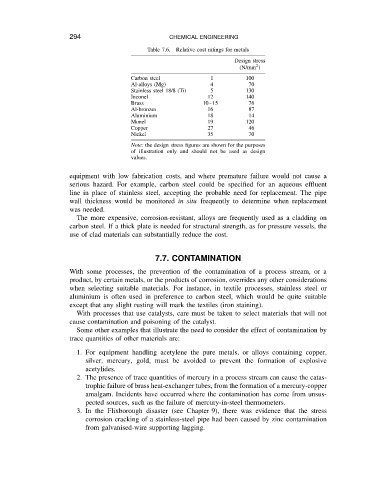
Relative cost ratings for metals
Table 7.6.
Design stress
2
(N/mm )
Carbon steel 1 100
Al-alloys (Mg) 4 70
Stainless steel 18/8 (Ti) 5 130
Inconel 12 140
Brass 10 15 76
Al-bronzes 16 87
Aluminium 18 14
Monel 19 120
Copper 27 46
Nickel 35 70
Note: the design stress figures are shown for the purposes
of illustration only and should not be used as design
values.
equipment with low fabrication costs, and where premature failure would not cause a
serious hazard. For example, carbon steel could be specified for an aqueous effluent
line in place of stainless steel, accepting the probable need for replacement. The pipe
wall thickness would be monitored in situ frequently to determine when replacement
was needed.
The more expensive, corrosion-resistant, alloys are frequently used as a cladding on
carbon steel. If a thick plate is needed for structural strength, as for pressure vessels, the
use of clad materials can substantially reduce the cost.
7.7. CONTAMINATION
With some processes, the prevention of the contamination of a process stream, or a
product, by certain metals, or the products of corrosion, overrides any other considerations
when selecting suitable materials. For instance, in textile processes, stainless steel or
aluminium is often used in preference to carbon steel, which would be quite suitable
except that any slight rusting will mark the textiles (iron staining).
With processes that use catalysts, care must be taken to select materials that will not
cause contamination and poisoning of the catalyst.
Some other examples that illustrate the need to consider the effect of contamination by
trace quantities of other materials are:
1. For equipment handling acetylene the pure metals, or alloys containing copper,
silver, mercury, gold, must be avoided to prevent the formation of explosive
acetylides.
2. The presence of trace quantities of mercury in a process stream can cause the catas-
trophic failure of brass heat-exchanger tubes, from the formation of a mercury-copper
amalgam. Incidents have occurred where the contamination has come from unsus-
pected sources, such as the failure of mercury-in-steel thermometers.
3. In the Flixborough disaster (see Chapter 9), there was evidence that the stress
corrosion cracking of a stainless-steel pipe had been caused by zinc contamination
from galvanised-wire supporting lagging.