Page 327 - Chemical engineering design
P. 327
302
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
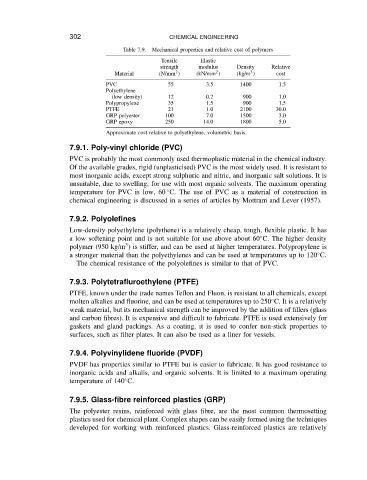
Mechanical properties and relative cost of polymers
Table 7.9.
Tensile Elastic
strength modulus Density Relative
2
3
2
Material (N/mm ) (kN/mm ) (kg/m ) cost
PVC 55 3.5 1400 1.5
Polyethylene
(low density) 12 0.2 900 1.0
Polypropylene 35 1.5 900 1.5
PTFE 21 1.0 2100 30.0
GRP polyester 100 7.0 1500 3.0
GRP epoxy 250 14.0 1800 5.0
Approximate cost relative to polyethylene, volumetric basis.
7.9.1. Poly-vinyl chloride (PVC)
PVC is probably the most commonly used thermoplastic material in the chemical industry.
Of the available grades, rigid (unplasticised) PVC is the most widely used. It is resistant to
most inorganic acids, except strong sulphuric and nitric, and inorganic salt solutions. It is
unsuitable, due to swelling, for use with most organic solvents. The maximum operating
Ž
temperature for PVC is low, 60 C. The use of PVC as a material of construction in
chemical engineering is discussed in a series of articles by Mottram and Lever (1957).
7.9.2. Polyolefines
Low-density polyethylene (polythene) is a relatively cheap, tough, flexible plastic. It has
Ž
a low softening point and is not suitable for use above about 60 C. The higher density
3
polymer (950 kg/m ) is stiffer, and can be used at higher temperatures. Polypropylene is
Ž
a stronger material than the polyethylenes and can be used at temperatures up to 120 C.
The chemical resistance of the polyolefines is similar to that of PVC.
7.9.3. Polytetrafluroethylene (PTFE)
PTFE, known under the trade names Teflon and Fluon, is resistant to all chemicals, except
Ž
molten alkalies and fluorine, and can be used at temperatures up to 250 C. It is a relatively
weak material, but its mechanical strength can be improved by the addition of fillers (glass
and carbon fibres). It is expensive and difficult to fabricate. PTFE is used extensively for
gaskets and gland packings. As a coating, it is used to confer non-stick properties to
surfaces, such as filter plates. It can also be used as a liner for vessels.
7.9.4. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF)
PVDF has properties similar to PTFE but is easier to fabricate. It has good resistance to
inorganic acids and alkalis, and organic solvents. It is limited to a maximum operating
Ž
temperature of 140 C.
7.9.5. Glass-fibre reinforced plastics (GRP)
The polyester resins, reinforced with glass fibre, are the most common thermosetting
plastics used for chemical plant. Complex shapes can be easily formed using the techniques
developed for working with reinforced plastics. Glass-reinforced plastics are relatively