Page 391 - Chemical engineering design
P. 391
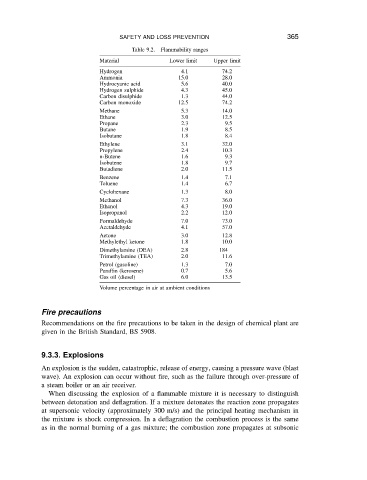
Table 9.2.
Flammability ranges
Material SAFETY AND LOSS PREVENTION Upper limit 365
Lower limit
Hydrogen 4.1 74.2
Ammonia 15.0 28.0
Hydrocyanic acid 5.6 40.0
Hydrogen sulphide 4.3 45.0
Carbon disulphide 1.3 44.0
Carbon monoxide 12.5 74.2
Methane 5.3 14.0
Ethane 3.0 12.5
Propane 2.3 9.5
Butane 1.9 8.5
Isobutane 1.8 8.4
Ethylene 3.1 32.0
Propylene 2.4 10.3
n-Butene 1.6 9.3
Isobutene 1.8 9.7
Butadiene 2.0 11.5
Benzene 1.4 7.1
Toluene 1.4 6.7
Cyclohexane 1.3 8.0
Methanol 7.3 36.0
Ethanol 4.3 19.0
Isopropanol 2.2 12.0
Formaldehyde 7.0 73.0
Acetaldehyde 4.1 57.0
Aetone 3.0 12.8
Methylethyl ketone 1.8 10.0
Dimethylamine (DEA) 2.8 184
Trimethylamine (TEA) 2.0 11.6
Petrol (gasoline) 1.3 7.0
Paraffin (kerosene) 0.7 5.6
Gas oil (diesel) 6.0 13.5
Volume percentage in air at ambient conditions
Fire precautions
Recommendations on the fire precautions to be taken in the design of chemical plant are
given in the British Standard, BS 5908.
9.3.3. Explosions
An explosion is the sudden, catastrophic, release of energy, causing a pressure wave (blast
wave). An explosion can occur without fire, such as the failure through over-pressure of
a steam boiler or an air receiver.
When discussing the explosion of a flammable mixture it is necessary to distinguish
between detonation and deflagration. If a mixture detonates the reaction zone propagates
at supersonic velocity (approximately 300 m/s) and the principal heating mechanism in
the mixture is shock compression. In a deflagration the combustion process is the same
as in the normal burning of a gas mixture; the combustion zone propagates at subsonic