Page 387 - Chemical process engineering design and economics
P. 387
Reactor Design 367
The next consideration is classifying reactors according to the phases in con-
tact. These are:
1. gas-liquid
2. liquid-liquid
3. gas-solid
4. liquid-solid
5. gas-liquid-solid
After specifying the energy form, the catalyst and the phases in contact, the
next task is to decide whether to conduct the reaction in a batch or continuous
mode. In the batch mode, the reactants are charged to a stirred-tank reactor (STR)
and allowed to react for a specified time. After completing the reaction, the reac-
tor is emptied to obtain the products. This operating mode is unsteady state.
Other unsteady-state reactors are: (1) continuous addition of one or more of the
reactants with no product withdrawal, and (2) all the reactants added at the begin-
ning with continuous withdrawal of product. At steady-state, reactants flow into
and products flow out continuously without a change in concentration and tem-
perature in the reactor.
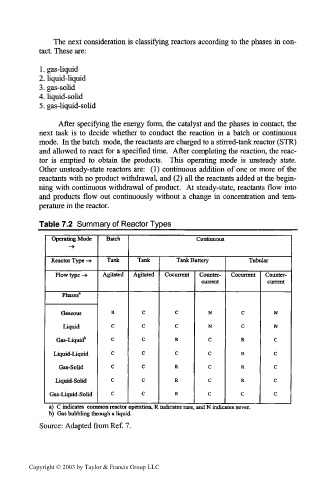
Table 7.2 Summary of Reactor Types
Operating Mode Batch Continuous
— »
Reactor Type -» Tank Tank Tank Battery Tubular
Flow type -» Agitated Agitated Cocurrent Counter- Cocurrent Counter-
current current
Phases'
Gaseous R C C N C N
Liquid C C C N C N
1
Gas-Liquid " C C R C R C
Liquid-Liquid C C C C R C
Gas-Solid C C R C R C
Liquid-Solid C C R C R C
Gas-Liquid-Solid C C R C C C
a) C indicates common reactor operation, R indicates rare, and N indicates never.
b) Gas bubbling through a liquid.
Source: Adapted from Ref. 7.
Copyright © 2003 by Taylor & Francis Group LLC