Page 393 - Chemical process engineering design and economics
P. 393
Reactor Design 373
Table 7.5 gives the calculation procedure. Any reaction kinetics, indicated by
Equation 7.4.4, can be used in the procedure. For each reactor in the series, we
assume
1. perfect mixing
2. constant volume
3. constant temperature
4. constant density
5. constant heat capacities
6. equal mixer power for each reactor
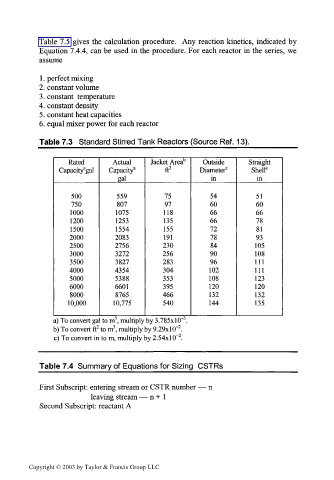
Table 7.3 Standard Stirred Tank Reactors (Source Ref. 13).
Rated Actual Jacket Area b Outside Straight
Capacitygal Capacity 3 ft 2 Diameter 0 Shell c
gal in in
500 559 75 54 51
750 807 97 60 60
1000 1075 118 66 66
1200 1253 135 66 78
1500 1554 155 72 81
2000 2083 191 78 93
2500 2756 230 84 105
3000 3272 256 90 108
3500 3827 283 96 111
4000 4354 304 102 111
5000 5388 353 108 123
6000 6601 395 120 120
8000 8765 466 132 132
10,000 10,775 540 144 135
3
a) To convert gal to m , multiply by 3.785x10
2
2
3
b) To convert ft to m , multiply by 9.29xlO" .
2
c) To convert in to m, multiply by 2.54xlO" .
Table 7.4 Summary of Equations for Sizing CSTRs
First Subscript: entering stream or CSTR number — n
leaving stream — n + 1
Second Subscript: reactant A
Copyright © 2003 by Taylor & Francis Group LLC