Page 52 - Chiral Separation Techniques
P. 52
28 2 Method Development and Optimization of Enantiomeric Separations Using …
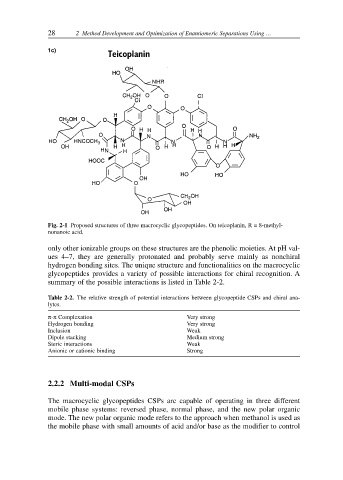
1c)
Fig. 2-1 Proposed structures of three macrocyclic glycopeptides. On teicoplanin, R = 8-methyl-
nonanoic acid.
only other ionizable groups on these structures are the phenolic moieties. At pH val-
ues 4–7, they are generally protonated and probably serve mainly as nonchiral
hydrogen bonding sites. The unique structure and functionalities on the macrocyclic
glycopeptides provides a variety of possible interactions for chiral recognition. A
summary of the possible interactions is listed in Table 2-2.
Table 2-2. The relative strength of potential interactions between glycopeptide CSPs and chiral ana-
lytes.
π-π Complexation Very strong
Hydrogen bonding Very strong
Inclusion Weak
Dipole stacking Medium strong
Steric interactions Weak
Anionic or cationic binding Strong
2.2.2 Multi-modal CSPs
The macrocyclic glycopeptides CSPs arc capable of operating in three different
mobile phase systems: reversed phase, normal phase, and the new polar organic
mode. The new polar organic mode refers to the approach when methanol is used as
the mobile phase with small amounts of acid and/or base as the modifier to control