Page 53 - Chiral Separation Techniques
P. 53
2.2 Characteristics of Macrocyclic Glycopeptide CSPs 29
selectivity. Since the macrocycles are covalently bonded to silica gel through multi-
ple linkages, there is no detrimental effect when a column switches from one mobile
phase system to another.
The enantioselectivity of the macrocyclic CSPs are different in each of the oper-
ating modes, probably because of different separation mechanisms functioning in
the different solvent modes. The possible chiral recognition mechanisms for three
mobile phase compositions on glycopeptide phases are listed in Table 2-3 in
descending order of strength.
Statistically, of the compounds enantioresolved by macrocyclic glycopeptide
CSPs, new polar organic mode accounts for more than 40 %, balanced by reversed-
phase mode, while typical normal-phase operation resulted in approximately 5 % of
separations. Some categories of racemic compounds that are resolved on the gly-
copeptide CSPs at different operating modes are listed in Table 2-4.
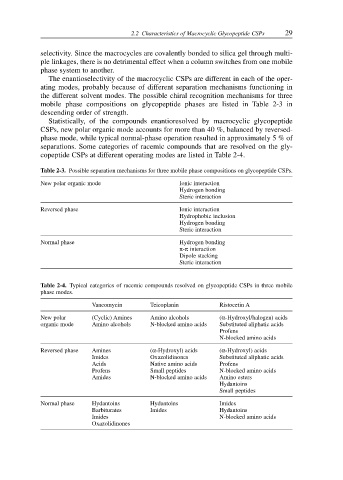
Table 2-3. Possible separation mechanisms for three mobile phase compositions on glycopeptide CSPs.
New polar organic mode Ionic interaction
Hydrogen bonding
Steric interaction
Reversed phase Ionic interaction
Hydrophobic inclusion
Hydrogen bonding
Steric interaction
Normal phase Hydrogen bonding
π-π interaction
Dipole stacking
Steric interaction
Table 2-4. Typical categories of racemic compounds resolved on glycopeptide CSPs in three mobile
phase modes.
Vancomycin Teicoplanin Ristocetin A
New polar (Cyclic) Amines Amino alcohols (α-Hydroxyl/halogen) acids
organic mode Amino alcohols N-blocked amino acids Substituted aliphatic acids
Profens
N-blocked amino acids
Reversed phase Amines (α-Hydroxyl) acids (α-Hydroxyl) acids
Imides Oxazolidinones Substituted aliphatic acids
Acids Native amino acids Profens
Profens Small peptides N-blocked amino acids
Amides N-blocked amino acids Amino esters
Hydantoins
Small peptides
Normal phase Hydantoins Hydantoins Imides
Barbiturates Imides Hydantoins
Imides N-blocked amino acids
Oxazolidinones