Page 129 - Civil Engineering Formulas
P. 129
BEAM FORMULAS 71
where L unbraced length of the member
E modulus of elasticity
I y moment of inertial about minor axis
G shear modulus of elasticity
J torsional constant
The critical moment is proportional to both the lateral bending stiffness EI y /L
and the torsional stiffness of the member GJ/L.
For the case of an open section, such as a wide-flange or I-beam section,
warping rigidity can provide additional torsional stiffness. Buckling of a simply
supported beam of open cross section subjected to uniform bending occurs at the
critical bending moment, given by
EI y GJ EC w
2
M cr (2.27)
L B L 2
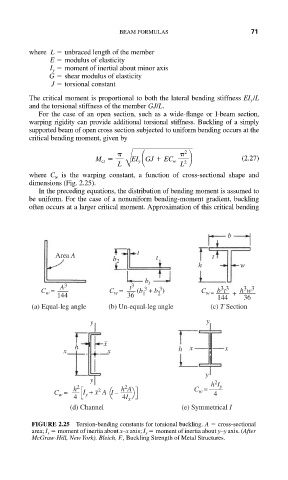
where C w is the warping constant, a function of cross-sectional shape and
dimensions (Fig. 2.25).
In the preceding equations, the distribution of bending moment is assumed to
be uniform. For the case of a nonuniform bending-moment gradient, buckling
often occurs at a larger critical moment. Approximation of this critical bending
b
t
Area A t t
b 2
h w
b t
A 3 t 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
C w = C w = (b + b ) C w = b t h w
144 36 1 2 144 + 36
(a) Equal-leg angle (b) Un-equal-leg angle (c) T Section
y y
–
h x x x
x x h
y
y 2
2
h 2 –2 h A C w = h I y
C w = I y + x A I – 4
4 4I x
(d) Channel (e) Symmetrical I
FIGURE 2.25 Torsion-bending constants for torsional buckling. A cross-sectional
area; I x moment of inertia about x–x axis; I y moment of inertia about y–y axis. (After
McGraw-Hill, New York). Bleich, F., Buckling Strength of Metal Structures.