Page 127 - Civil Engineering Formulas
P. 127
BEAM FORMULAS 69
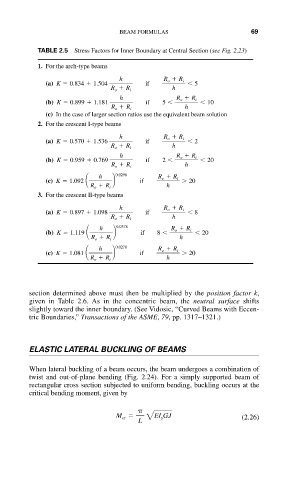
TABLE 2.5 Stress Factors for Inner Boundary at Central Section (see Fig. 2.23)
1. For the arch-type beams
h if R o R i
(a) K 0.834 1.504 5
R o R i h
h R o R i
(b) K 0.899 1.181 if 5 10
R o R i h
(c) In the case of larger section ratios use the equivalent beam solution
2. For the crescent I-type beams
h if R o R i
(a) K 0.570 1.536 2
R o R i h
h R o R i
(b) K 0.959 0.769 if 2 20
R o R i h
h 0.0298 if R o R i
(c) K 1.092 20
R o R i h
3. For the crescent II-type beams
h if R o R i
(a) K 0.897 1.098 8
R o R i h
h 0.0378 R o R i
(b) K 1.119 if 8 20
R o R i h
h 0.0270 if R o R i
(c) K 1.081 20
R o R i h
section determined above must then be multiplied by the position factor k,
given in Table 2.6. As in the concentric beam, the neutral surface shifts
slightly toward the inner boundary. (See Vidosic, “Curved Beams with Eccen-
tric Boundaries,” Transactions of the ASME, 79, pp. 1317–1321.)
ELASTIC LATERAL BUCKLING OF BEAMS
When lateral buckling of a beam occurs, the beam undergoes a combination of
twist and out-of-plane bending (Fig. 2.24). For a simply supported beam of
rectangular cross section subjected to uniform bending, buckling occurs at the
critical bending moment, given by
M cr 2 EI y GJ (2.26)
L