Page 341 - Civil Engineering Formulas
P. 341
272 CHAPTER TEN
If elastic elongation and can be ignored,
1
M L dx 1
3
H L 0 M L dx (10.95)
1 2 fl 0
y D dx
0
Thus, for a load uniformly distributed horizontally w ,
L
1 w L l 3
M L dx (10.96)
0 12
and the increase in the horizontal component of tension due to live load is
3 w L l 3 w L l 2 w L l 2 8H D
H L (10.97)
2 fl 12 8 f 8 w D l 2
w L
H D (10.98)
w D
CABLE SYSTEMS
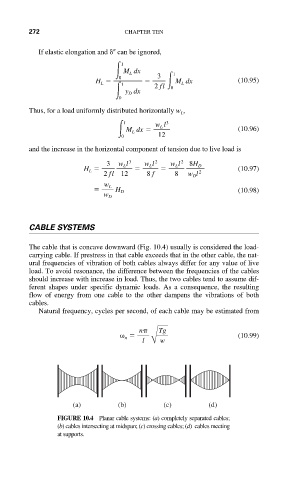
The cable that is concave downward (Fig. 10.4) usually is considered the load-
carrying cable. If prestress in that cable exceeds that in the other cable, the nat-
ural frequencies of vibration of both cables always differ for any value of live
load. To avoid resonance, the difference between the frequencies of the cables
should increase with increase in load. Thus, the two cables tend to assume dif-
ferent shapes under specific dynamic loads. As a consequence, the resulting
flow of energy from one cable to the other dampens the vibrations of both
cables.
Natural frequency, cycles per second, of each cable may be estimated from
n
Tg
n (10.99)
l B w
(a) (b) (c) (d)
FIGURE 10.4 Planar cable systems: (a) completely separated cables;
(b) cables intersecting at midspan; (c) crossing cables; (d) cables meeting
at supports.