Page 184 - Classification Parameter Estimation & State Estimation An Engg Approach Using MATLAB
P. 184
NONPARAMETRIC LEARNING 173
(a) (b)
1 0.8
1
measure of eccentricity 0.6 measure of eccentricity 0.6
0.8
0.4
0.4
0.2
0 0.2
0
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
measure of six-fold rotational symmetry measure of six-fold rotational symmetry
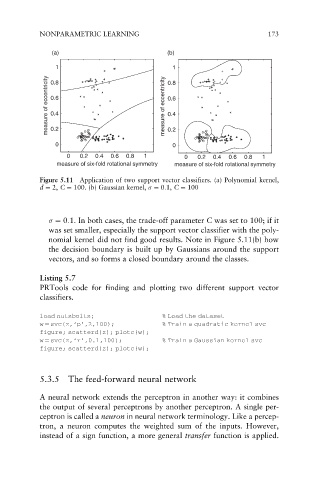
Figure 5.11 Application of two support vector classifiers. (a) Polynomial kernel,
d ¼ 2, C ¼ 100. (b) Gaussian kernel, ¼ 0:1, C ¼ 100
¼ 0:1. In both cases, the trade-off parameter C was set to 100; if it
was set smaller, especially the support vector classifier with the poly-
nomial kernel did not find good results. Note in Figure 5.11(b) how
the decision boundary is built up by Gaussians around the support
vectors, and so forms a closed boundary around the classes.
Listing 5.7
PRTools code for finding and plotting two different support vector
classifiers.
load nutsbolts; % Load the dataset
w ¼ svc(z,‘p’,2,100); % Train a quadratic kernel svc
figure; scatterd(z); plotc(w);
w ¼ svc(z,‘r’,0.1,100); % Train a Gaussian kernel svc
figure; scatterd(z); plotc(w);
5.3.5 The feed-forward neural network
A neural network extends the perceptron in another way: it combines
the output of several perceptrons by another perceptron. A single per-
ceptron is called a neuron in neural network terminology. Like a percep-
tron, a neuron computes the weighted sum of the inputs. However,
instead of a sign function, a more general transfer function is applied.