Page 185 - Classification Parameter Estimation & State Estimation An Engg Approach Using MATLAB
P. 185
174 SUPERVISED LEARNING
A transfer function used often is the sigmoid function, a continuous
version of the sign function:
1
T
gðyÞ¼ fðw yÞ¼ T ð5:62Þ
1 þ expð w yÞ
where y is the vector z augmented with a constant value 1. The vector
w is called the weight vector, and the specific weight corresponding to
the constant value 1 in z is called the bias weight.
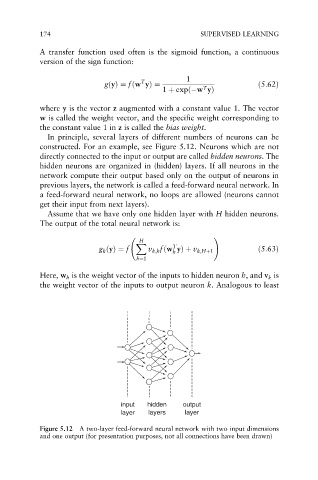
In principle, several layers of different numbers of neurons can be
constructed. For an example, see Figure 5.12. Neurons which are not
directly connected to the input or output are called hidden neurons. The
hidden neurons are organized in (hidden) layers. If all neurons in the
network compute their output based only on the output of neurons in
previous layers, the network is called a feed-forward neural network. In
a feed-forward neural network, no loops are allowed (neurons cannot
get their input from next layers).
Assume that we have only one hidden layer with H hidden neurons.
The output of the total neural network is:
!
H
X
g k ðyÞ¼ f T ð5:63Þ
v k;h fðw yÞþ v k;Hþ1
h
h¼1
Here, w h is the weight vector of the inputs to hidden neuron h, and v k is
the weight vector of the inputs to output neuron k. Analogous to least
input hidden output
layer layers layer
Figure 5.12 A two-layer feed-forward neural network with two input dimensions
and one output (for presentation purposes, not all connections have been drawn)