Page 206 - Color Atlas of Biochemistry
P. 206
Basics 197
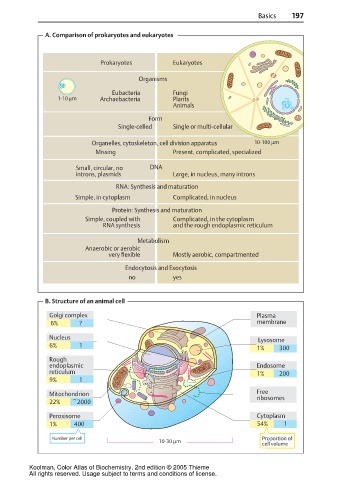
A. Comparison of prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Prokaryotes Eukaryotes
Organisms
Eubacteria Fungi
1-10 µm Archaebacteria Plants
Animals
Form
Single-celled Single or multi-cellular
Organelles, cytoskeleton, cell division apparatus 10-100 µm
Missing Present, complicated, specialized
Small, circular, no DNA
introns, plasmids Large, in nucleus, many introns
RNA: Synthesis and maturation
Simple, in cytoplasm Complicated, in nucleus
Protein: Synthesis and maturation
Simple, coupled with Complicated, in the cytoplasm
RNA synthesis and the rough endoplasmic reticulum
Metabolism
Anaerobic or aerobic
very flexible Mostly aerobic, compartmented
Endocytosis and Exocytosis
no yes
B. Structure of an animal cell
Golgi complex Plasma
6% ? membrane
Nucleus
Lysosome
6% 1
1% 300
Rough
endoplasmic Endosome
reticulum 1% 200
9% 1
Mitochondrion Free
ribosomes
22% ~2000
Peroxisome Cytoplasm
1% 400 54% 1
Number per cell Proportion of
10-30 µm
cell volume
Koolman, Color Atlas of Biochemistry, 2nd edition © 2005 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.