Page 181 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 181
angular speed =
17 degrees
per second
Y = 75 degrees; Z = 51 degrees; Joystick
angular speed =
25 degrees
per second
X = 39 degrees;
angular speed =
End point reached
13 degrees in 3 seconds
per second
Joint-interpolated motion
which together define the set of all possible positions the device can attain.
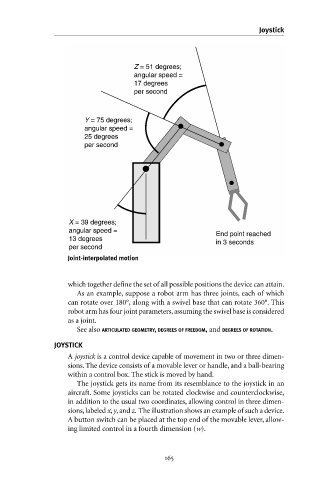
As an example, suppose a robot arm has three joints, each of which
can rotate over 180°, along with a swivel base that can rotate 360°. This
robot arm has four joint parameters,assuming the swivel base is considered
as a joint.
See also ARTICULATED GEOMETRY, DEGREES OF FREEDOM, and DEGREES OF ROTATION.
JOYSTICK
A joystick is a control device capable of movement in two or three dimen-
sions. The device consists of a movable lever or handle, and a ball-bearing
within a control box. The stick is moved by hand.
The joystick gets its name from its resemblance to the joystick in an
aircraft. Some joysticks can be rotated clockwise and counterclockwise,
in addition to the usual two coordinates, allowing control in three dimen-
sions,labeled x,y,and z. The illustration shows an example of such a device.
A button switch can be placed at the top end of the movable lever, allow-
ing limited control in a fourth dimension (w).