Page 201 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 201
Magnitude Profile
MAGNITUDE PROFILE
The term magnitude profile refers to the way in which a robot behaves near
an object of interest. In particular, the term refers to the variation in the
length (magnitude) of a vector, depending on the distance (radius) from
the object of interest.The vector magnitude might represent the output level
from a proximity sensor or distance-measurement device,or the robot’s speed
or acceleration in a particular direction relative to the object of interest.
As an example, suppose a robot is equipped with a proximity sensor
designed to warn it when obstructions are nearby. The output from the
sensor increases as the distance between the robot and the object decreases.
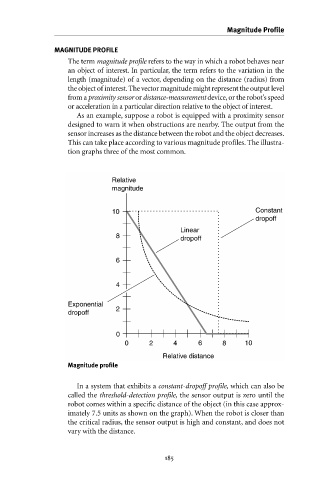
This can take place according to various magnitude profiles. The illustra-
tion graphs three of the most common.
Relative
magnitude
10 Constant
dropoff
Linear
8 dropoff
6
4
Exponential
2
dropoff
0
0 2 4 6 8 10
Relative distance
Magnitude profile
In a system that exhibits a constant-dropoff profile, which can also be
called the threshold-detection profile, the sensor output is zero until the
robot comes within a specific distance of the object (in this case approx-
imately 7.5 units as shown on the graph). When the robot is closer than
the critical radius, the sensor output is high and constant, and does not
vary with the distance.